How to Create Search Engine-friendly Internationalized Web Apps with Angular Universal and ngx-translate
Time to read:
This post is part of Twilio’s archive and may contain outdated information. We’re always building something new, so be sure to check out our latest posts for the most up-to-date insights.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is important for many Angular single-page applications (SPAs). You can build SEO-friendly Angular websites with Angular Universal, but how do you make your app SEO-friendly in every language your website supports? Google, Yandex, and Baidu, might request your pages in English, Spanish, Russian, or Chinese: how do you make your server-side rendering return the correct language?
The answer is ngx-translate, the internationalization (i18n) and localization library for Angular. This module makes it easy to use translation files that provide the correct language for both client-side and server-side rendering. This post will show you how to use it.
In this post we will:
- Create an Angular application with one component, the home page
- Add server-side rendering for SEO purposes with Angular Universal
- Set up internationalization in four languages with ngx-translate
To accomplish the tasks in this post you will need to install the following:
- Node.js and npm (The Node.js installation will also install npm.)
- Angular CLI
Set up the Angular project and run Hello World!
Every Angular project begins with installation and initialization of the packages. Type the following at the command prompt:
When the project is initialized, navigate to its directory:
And run the application by typing:
You should see following output in the console:
The -o flag will open the application in your default browser. (In Chrome version 63 or higher you must set flags to open HTTP links and sites without a valid security certificate, such as localhost). You can navigate manually to the URL provided in the command output.
You should see the following screen in your browser:

Implement server-side rendering with Angular Universal
Now we are ready to add server-side rendering to our application with Angular Universal, a technology that renders web pages on the server so your site’s pages can be quickly and easily read by a search engine crawler. To install it, execute this command:
Verify server-side rendering is working
Check to see if Angular Universal is working correctly by running the app and performing a curl request on it:
If you don’t want to use curl you can open the URL in a browser and inspect the page source. The results, as follows, should be the same:
If you want to catch up to this step:
Add internationalization to the app with ngx-translate
Let’s make our application more friendly for users around the world. To achieve that, we are going to add internationalization (i18n) to it with the ngx-translate library. We will provide our website visitors with clickable links they can use to switch between different translations. Those translations will be loaded from .json files for each language by ngx-translate. For each translate key in our app.component.html template a translated value will be injected.
The first step is installation of dependencies:
Create the following file structure for the translations:
Place the following key-value pairs in each file. For src/assets/i18n/en.json:
src/assets/i18n/es.json:
src/assets/i18n/ru.json:
src/assets/i18n/zh.json:
We have provided translations in four languages. Now we’ll implement the translation mechanism in our application. Import the ngx-translate module and translations loader by replacing the contents of src/app/app.browser.module.ts with the following code:
What we did here is import HttpClientModule from the @angular/common/http library. We need it to provide an HttpClient, which is injected into the factory method and used for loading translation files using HTTP requests:
Finally, we import the TranslateModule and provide our loader into it:
We also need to import TranslateModule into the src/app/app.module.ts file:
Replace the code in the src/app/app.component.html template with the following to provide translation keys and links for switching between languages:
The final step in providing internationalization in the browser-side code is to implement the switchLanguage method in our component and provide default translations for the active region. Make following changes in the src/app/app.component.ts:
We got it! Internationalization on the browser side is implemented! Let’s check it out:
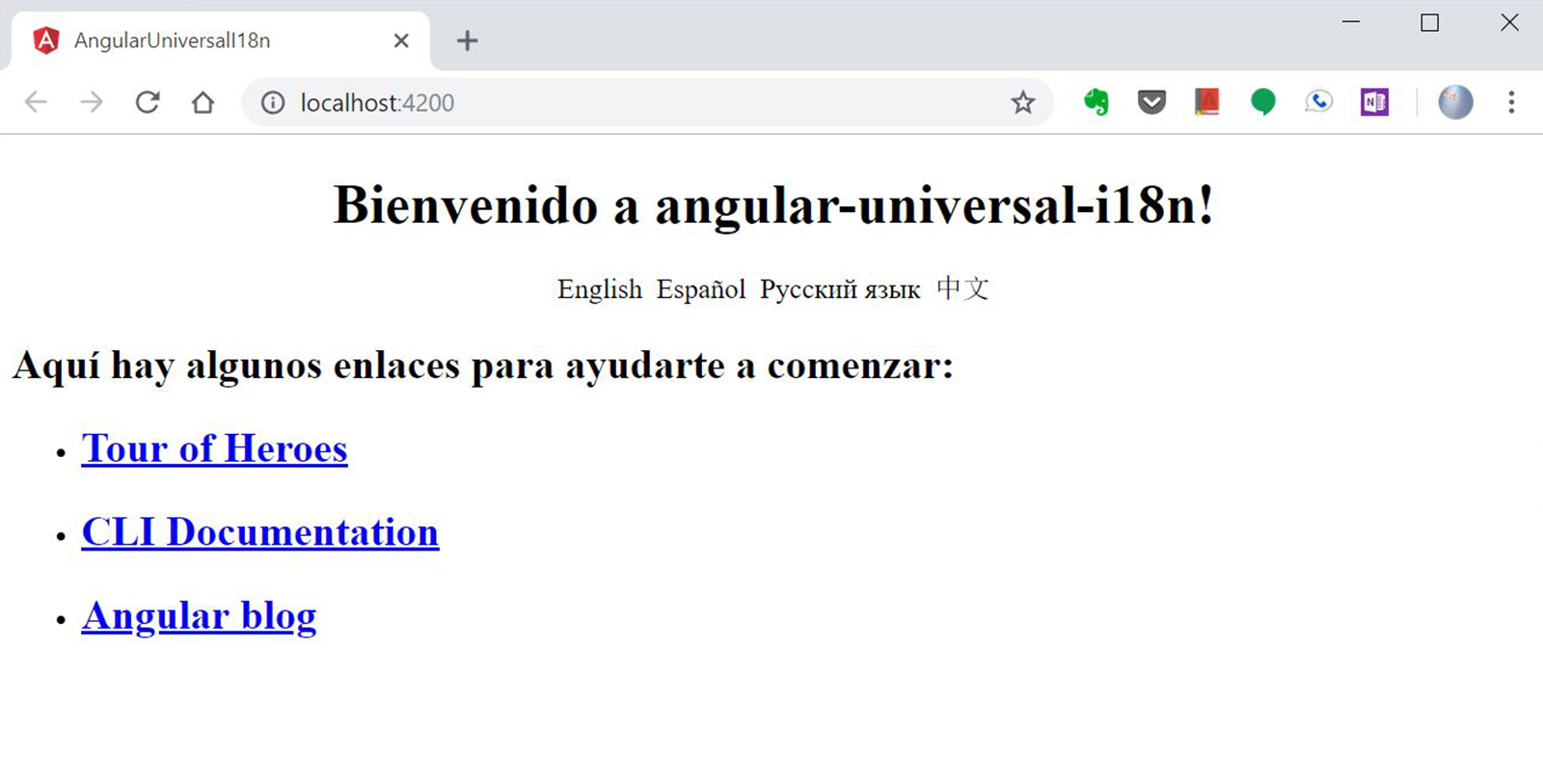
After navigating to http://localhost:4200 and changing the selected language to Español we can see:
If you want to catch up to this step:
Add server-side internationalization
Check to see if our client-side implementation broke anything on the server side. Start the app in server mode by running the following commands:
After navigating to http://localhost:8080 we can see that our app is no longer working:
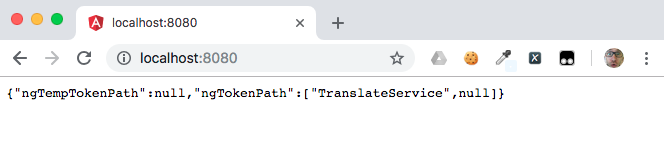
More error information can be seen in the console:
To fix this issue we need to provide TranslateModule in the server module as well. Make following changes in the src/app/app.server.module.ts:
We also need to make changes in src/app/app.component.ts to implement i18n on the server side. Replace the contents with the following code:
The additional code determines the current language for the user agent by reading the HTTP accept-language header sent by user agent (browser or web crawler) when requesting the page at the URI specified by the user agent. To retrieve this header we need to inject a @REQUEST provided in @nguniversal/express-engine/tokens.
After that we determine if we are executing code on the browser side or server side by using the isPlatformBrowser method together with the @PLATFORM_ID token. If we are on the browser side we set the language in the same way as previously, by retrieving it from the translate service. If we are on the server side we read it from the header with:
We also need to make small change in the typescript configuration file, src/tsconfig.app.json:
We added the node value to the types section. We need that because we are using fs to load translation files directly from the file-system when we are performing server-side rendering.
Test server-side internationalization rendering
We are done with translations on the server side. Check it out by running the application and performing a curl request with a customized header. Build and run the app as follows:
Then make the curl request specifying Russian (ru_RU) as the current user agent language:
Alternately, you can inspect the page source in your browser’s developer tools after clicking Pусский язык on the home page. Note, however, that using “View page source” will reload the page and show you the English (or your default) language version.
The results should look like this:
Yay! As we expect, our website is rendered on the server side, and the Russian translations have been applied!
If you want to catch up to this step:
Summary
Today we covered an important challenge for all mature applications: internationalization. As you can see; you can bring internationalization to server-side rendering, making your application search engine optimized in every language that you support.
If you want to learn more about Angular Universal techniques, check out my post on the Twilio blog: Getting Started with Serverless Angular Universal on AWS Lambda.
The GitHub repository, for the code used in this post can be found here: https://github.com/maciejtreder/angular-universal-i18n. You can also contact me via contact@maciejtreder.com, https://www.maciejtreder.com or @maciejtreder (GitHub, Twitter, StackOverflow, LinkedIn).
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


