How to make Phone Calls from Blazor WebAssembly with Twilio Voice
Time to read:

Mobile phones are ubiquitous and convenient but there are times when it’s more practical to be able to receive and place phone calls from a computer. If you’ve called customer service about the tickets you ordered, or anything else, it’s likely the rep you spoke to took your call with a mouse click.
Using Twilio Voice you can add the ability to make and receive phone calls from your own ASP.NET web applications. Twilio’s helper library for JavaScript makes it easy to integrate client functionality into web front ends built with Blazor WebAssembly, and the Twilio NuGet packages provide you with convenient interfaces to Twilio’s APIs for server-side tasks.
Blazor WebAssembly lets you build your application front end in C# and Razor, so you can focus the client-side JavaScript on functionality that requires JavaScript for implementation.
JavaScript interoperability (JS interop) is a feature of Blazor that makes it easy to call JavaScript APIs and libraries from your C# code.
Both these technologies are built on .NET Standard, so they’re available in both ASP.NET Core 3.1 and ASP.NET Core in .NET 5.0.
In this post you’ll learn how to build a web application for making and receiving voice calls using these technologies. You’ll see how to integrate a Blazor component with the Twilio Client JS SDK and how to route Twilio calls using ASP.NET Core WebAPI. You’ll also learn how to use TwiML™ (the Twilio Markup Language) to tell Twilio what to do when a call comes into a Twilio phone number.
The tutorial in this post contains the complete source code and it’s provided under an MIT license so you can incorporate it into your own project.
Prerequisites
This tutorial is for developers at any experience level. Prior experience with the following technologies is recommended, but not required:
- C#
- .NET and ASP.NET Core
- HTML
- JavaScript
- Blazor
You’ll need the following development resources to build and run the project:
.NET Core SDK version 3.1 or .NET 5.0
Code editor – Any editor will suffice, but for an optimal experience use:
Visual Studio Code with the C# for Visual Studio Code extension.
– or –
Visual Studio 2019 (The Community edition is free.) with the following workloads enabled: ASP.NET and web development, .NET Core cross-platform development.
PowerShell – You can use the latest PowerShell Core or the legacy Windows version.
Twilio account – Sign up for a free trial account (no credit card required) and use promotional credit to try out Twilio products.
Twilio CLI – The Twilio command-line interface requires Node.js and npm (included with the Node.js installation).
ngrok – A free account is all that’s necessary.
There is a companion repository available on GitHub for this tutorial. It contains the complete code for the solution you’re going to build.
Understanding the use case
The goal of this application is to build a working single page Blazor WebAssembly application you can use to make and receive phone calls while still being able to interact with the application. To accomplish this, you will create a dialer component which will be docked on the bottom right of the screen.
Here’s a screenshot of the end result:
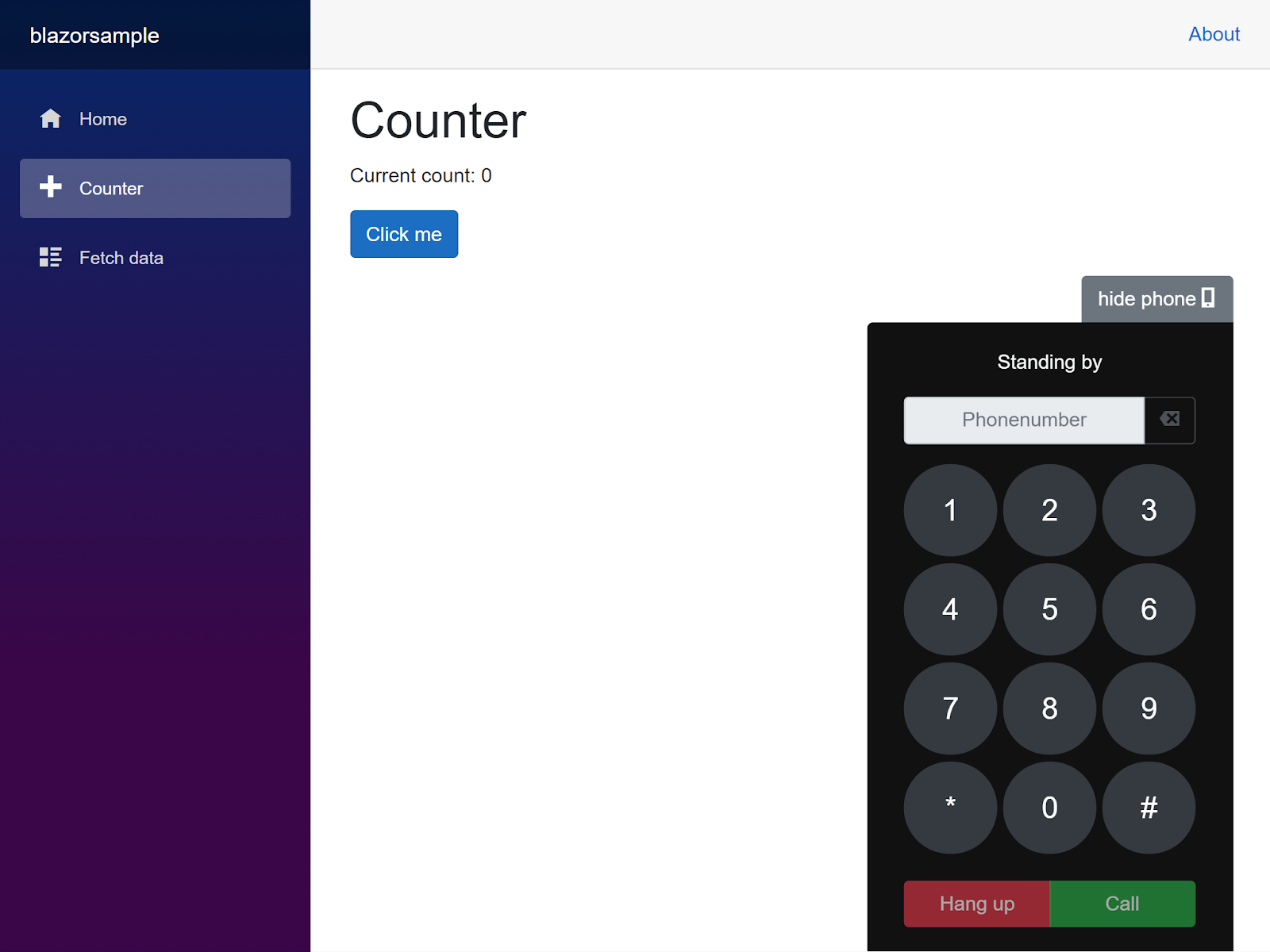
Here’s an animation of the dialer in action:
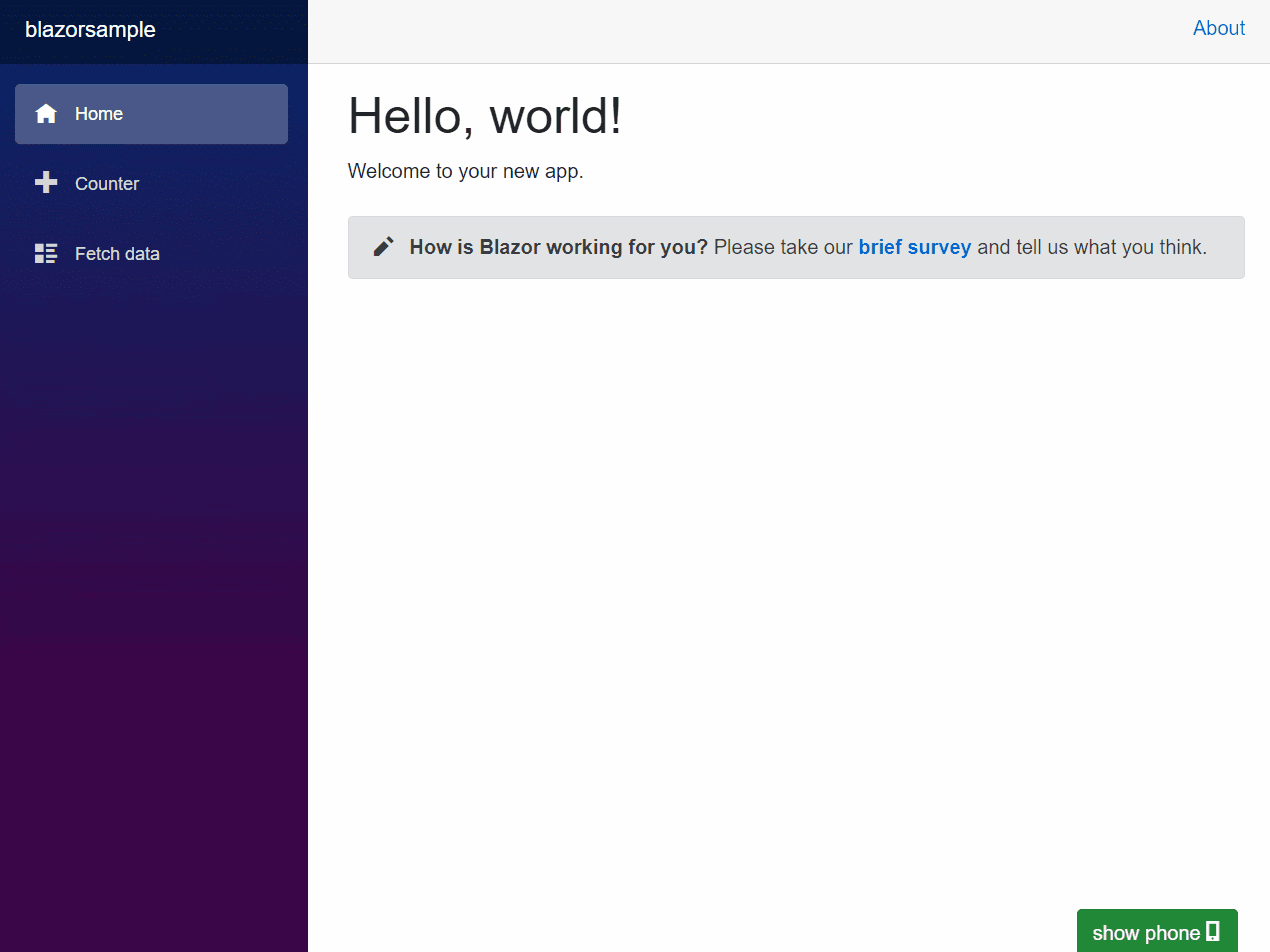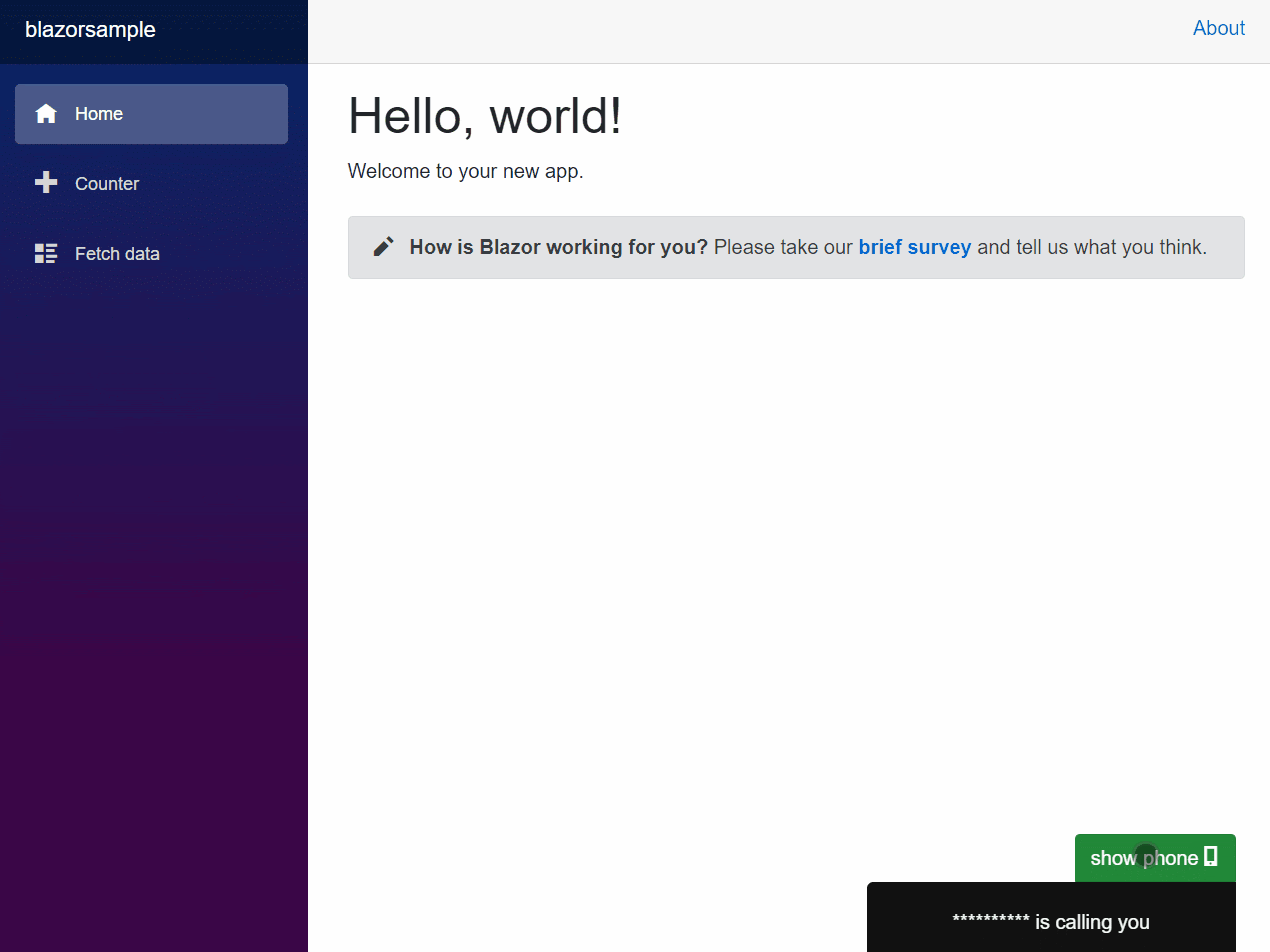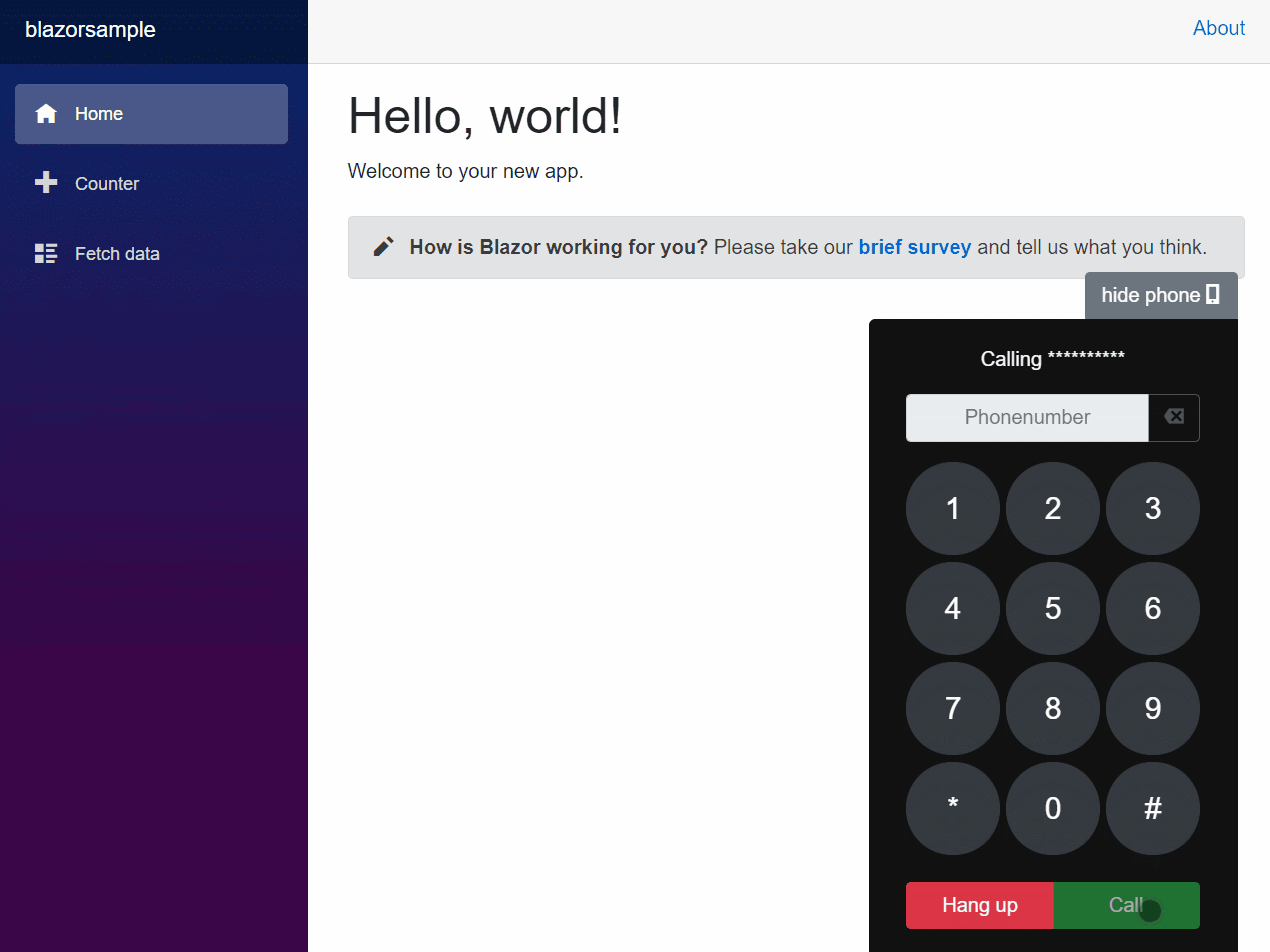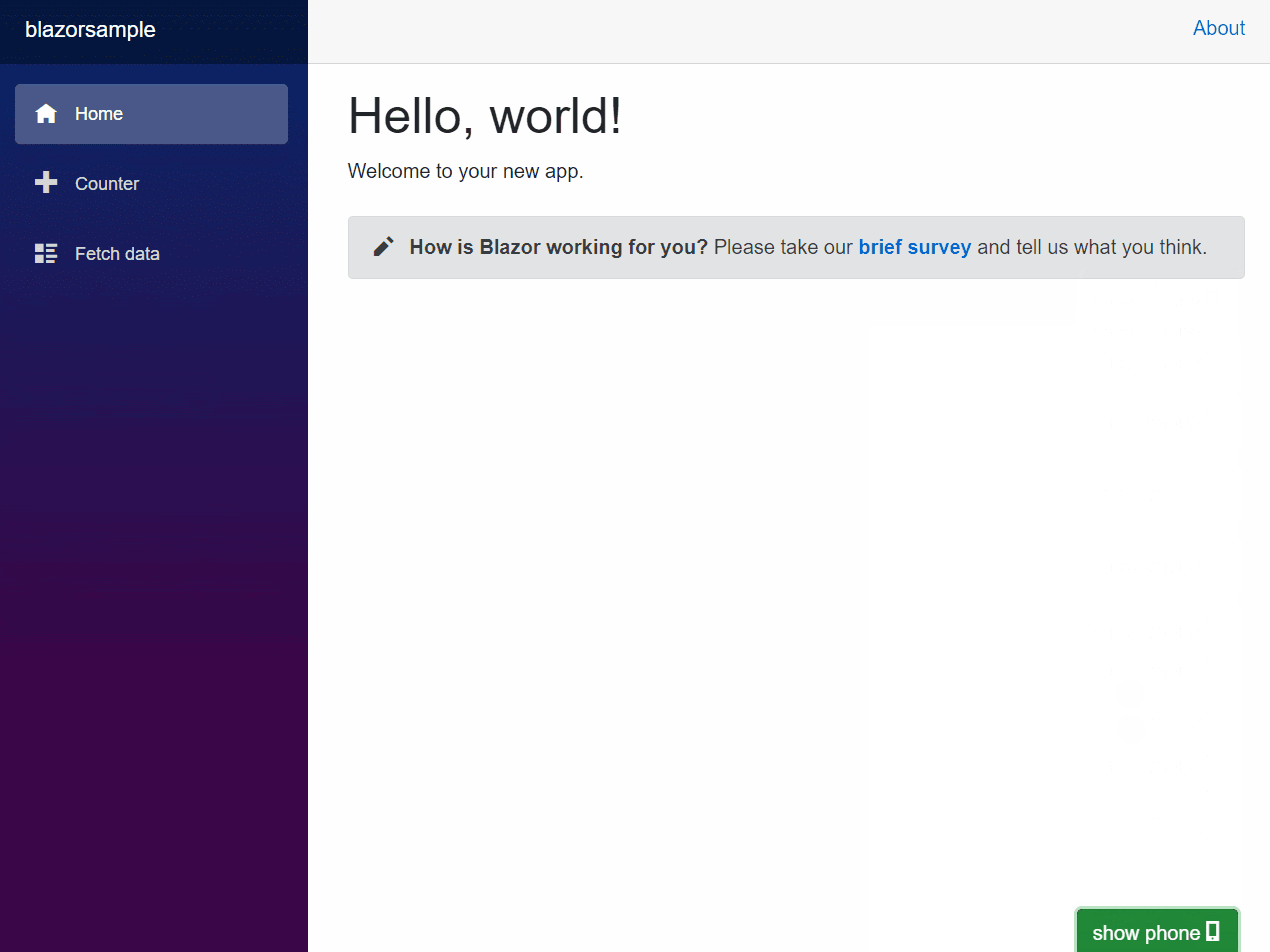
You can use the dialer to dial phone numbers and call them. If a call is incoming, the dialer will vibrate to raise awareness of an incoming call to the user. (The phone numbers will be masked in the screenshots for privacy reasons.)
Solution architecture
The solution will consist of a client application implemented in Blazor WebAssembly and a server application implemented in ASP.NET Core. The client application will fetch an authentication token from the server, which will be used to authenticate the client with the Twilio service. Once authenticated, the client can initiate and receive calls routed through Twilio Voice. When an outgoing or incoming call is made, Twilio will reach out to the server application to receive instructions, written in TwiML, on how to handle the call.
Generating auth tokens to connect to Twilio
Before you can connect to Twilio using the Twilio Client JS SDK you need to get an authentication token. You can request this auth token by making AJAX requests to your server application and have it generate the token. The auth token will hold the following configuration:
- A Twilio Account String IDentifier (SID)
- A boolean to opt into incoming voice calls
- An identity string which is used as the client name – The client name is used to route incoming calls to the Twilio Client.
- A TwiML Application SID for outgoing voice calls – The TwiML App SID identifies a TwiML app, which holds an SMS Webhook URL and a Voice Webhook URL. These webhooks are how Twilio knows which URLs to send HTTP requests to when you initiate a call using the JavaScript SDK.
Warning: In this tutorial anyone will be able to request these authentication tokens, which is a security risk. When implementing a token service, add your own authentication and authorization logic to make sure you generate tokens only for those who are supposed to be able to make phone calls using your application.
Making outgoing phone calls (from browser to phone)
You can make outgoing phone calls using the Twilio Client JS SDK and a backend responding to webhooks. The workflow to make outgoing phone calls goes as follows:
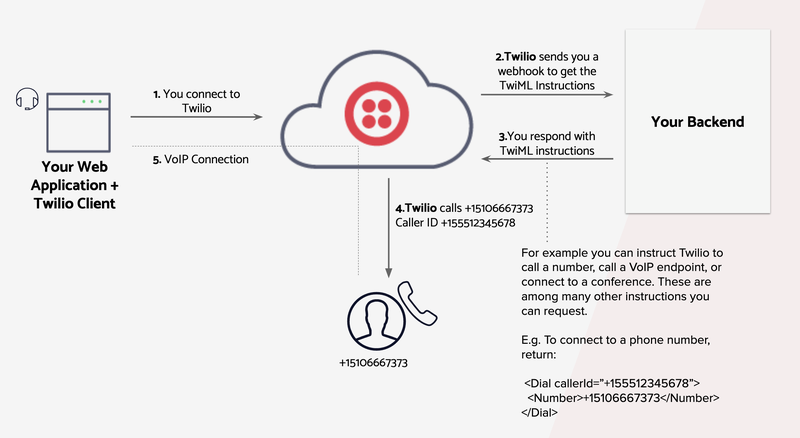
Figure 1: Workflow diagram for outgoing phone calls (source: Twilio documentation)
- Using the Twilio Client JS SDK, the browser connects to Twilio using a previously generated authentication token. Twilio decrypts this authentication token and reads the outgoing client scope, which holds a TwiML App SID. With this TwiML App SID, Twilio can fetch the voice webhook configured in your TwiML App.
- Twilio sends an HTTP request to the voice webhook configured in your TwiML App. This HTTP request holds metadata you can use to determine who to route the phone call to.
- Your server application returns TwiML instructions in the HTTP response to dial the desired number.
- Twilio will read your TwiML response and dial the phone number.
- The Twilio Client JS SDK will establish the VoIP connection between your browser and the phone number.
Receiving incoming phone calls (from phone to browser)
You can also receive incoming phone calls using the Twilio Client JS SDK and a WebAPI server application responding to webhooks. The workflow for an incoming phone call goes as follows:
- Your Twilio phone number is called and is received by Twilio Voice.
- Twilio makes an HTTP request to the voice webhook URL configured on your Twilio phone number. This webhook URL is configured on your phone number, not your TwiML App voice webhook.
- Your server application responds with TwiML instructions. For outgoing phone calls you instruct Twilio to <Dial> a <Number>, but for the incoming phone call you want the call to be routed to the browser client. To do so, you have to instruct Twilio to <Dial> a <Client>. The specified Client should match the client in the incoming client scope part of the authentication token.
- Twilio will read your TwiML response and dial the client. If no client is connected, the phone call is closed. If multiple clients are connected, the first to accept the call will establish the VoIP connection and other clients will stop ringing.
- The Twilio JavaScript SDK will establish the VoIP connection between the client and the phone number.
Creating Twilio resources
You need to create the following Twilio resources to be able to make and receive phone calls from the browser:
You can create these resources with the Twilio CLI or the Twilio console web interface.
Install the Twilio CLI on your machine by following the Twilio CLI Quickstart instructions.
Log in using the Twilio CLI using the following command:
You will be prompted to enter your Account SID and Auth Token. Both can be found on the right-hand side of the Twilio console home page.
Copy your Account SID and Auth Token someplace handy. You will need them later. They’re user secrets, so be sure to handle them securely. (For example, don’t put them in your source code.)
The server application will need a Twilio API key and secret. Browse to API Keys in the Twilio console and create a standard API key.
Copy the SID, which is the API key, and the secret someplace handy and secure. These are also user secrets, so take all the appropriate precautions.
If you don’t have a Twilio phone number, you can get a local phone number using the following command, replacing “US” with the appropriate country code for your location:
Note: Although you’ll be buying a phone number, the credit in your trial account will be applied to the charge. No credit card is required.
If you already have a Twilio phone number, you can list your phone numbers using the following command:
Copy the phone number that you want to use for this application someplace handy.
Run the following command to create a TwiML application:
You can give the application any friendly name that is meaningful to you.
If you already created a TwiML application, you can list your applications using the following command:
Copy the TwiML application SID someplace handy and secure.
You will need to configure the voice webhook URL later, but you don’t have a backend or public URL to configure it with yet.
Now you should have all of the following noted on the side for future use:
- Account SID and Auth Token
- API Key and Secret
- Phone Number
- TwiML Application SID
Building the Twilio authentication token server
The token authentication server is the first of two C# projects you’ll create in this tutorial. It will be the backend server for the client, supplying authentication tokens obtained from Twilio. It will also handle Twilio webhooks.
In a production-grade application, it would be better if you create an internal backend and a publicly available server dedicated to handling Twilio webhooks. For the sake of simplicity, this tutorial combines these functions in a single server.
Create the ASP.NET Core WebAPI application
The token authentication server will be implemented as an ASP.NET Core WebAPI project. Using this platform, it will also provide REST APIs the Twilio webhooks will call.
Use the following commands to create the server project:
Later on, you’ll create a client application which will try to use the same ports by default (5000 and 5001) which is not possible. Use the following commands to change the used ports to 5002 and 5003 by updating the launchSettings.json file at TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server/Properties/launchSettings.json.
You can run your server project using this command:
If you’re using Visual Studio to run your projects, use the Kestrel target instead of IIS Express.
For your convenience, you can also use the dotnet watch run alternative. This will automatically reload the .NET application as you edit. You can use this command to watch your project:
By default, the ASP.NET Core Web API template comes with an existing controller and a model class. Remove the files for these classes:
Configure user secrets
The server project will require access to all the previously noted configuration data, but you shouldn’t store this sensitive information directly inside the server project, which might cause accidental check-ins to source code control. 😱
Instead, you can use the dotnet user-secrets commands for the Secret Manager to store the configuration in secret storage.
Paste the following PowerShell commands and enter the prompted configuration:
You will be prompted to provide the configuration you noted earlier and each prompt will be stored in .NET’s secret storage. ASP.NET Core loads in configuration from secret storage out of the box during development.
You can list the secrets using the dotnet user-secrets list. Learn more about dotnet user-secrets in Safe storage of app secrets in development in ASP.NET Core on docs.microsoft.com.
Warning: The secrets are stored in plaintext in a file, secrets.json, in secret storage, and listing the secrets will display them in plaintext too. .NET’s secret storage is a tool for development purposes only.
Create a controller to generate Twilio authentication tokens
The browser application will need to connect to Twilio. To do so it will need an authentication token. In this section, you’ll create a controller and an action to generate authentication tokens which can be used to connect to Twilio.
Install the Twilio NuGet package with the VS 2019 Package Manager, Package Manager Console, or the following .NET CLI command:
The Twilio REST API helper library in this package contains the necessary classes to generate these authentication tokens.
Create the following controller at TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server\Controllers\TokenController.cs with the following contents:
An instance of the IConfiguration object is injected into the constructor by ASP.NET Core’s built-in dependency injection and then stored in a field. The TwilioAccountSid, TwilioApiKey, TwilioApiSecret, and TwiMLApplicationSid are all extracted from the configuration object.
When you create a Token, you can pass in different grants to provide access to specific Twilio functionality. The VoiceGrant will give the client access to the voice calling capabilities in Twilio and use your TwiML app to route outgoing voice calls. By setting IncomingAllow to true, you enable incoming voice calls.
You can quickly verify whether this works by running the server and making an HTTP request to https://localhost:5003/token.
Start the server:
Open a separate shell and run the following line to make an HTTP request to the token controller:
The response status code should be 200, and you can find the encrypted authentication token in the Content property.
Configure Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
The client will request the authentication token from within the browser. By default, the browser will not allow this due to Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) security measures.
To explicitly allow the client to make CORS requests, modify the server Startup class in TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server\Startup.cs by adding CORS Middleware with a named policy.
Locate the following statement in the ConfigureServices method:
Insert the following code immediately above:
In the Configure method, locate the following statement:
Add the following line immediately above:
A CORS policy has been configured in the Startup class, but you need to add the EnableCorsAttribute to TokenController.Get method for the CORS policy to apply.
In the Controllers/TokenController.cs file, modify the TokenController class by adding the following using directive for CORS:
Decorate the `Get` method with the EnableCors attribute so the beginning of the class looks like the following:
Ellipsis (“...”) in the preceding code block indicates a section redacted for brevity.
You can verify this works by simulating a CORS preflight check.
Start the server:
Open a separate shell and run the following command to make an HTTP request simulating a CORS request against the token controller:
The response should contain this header:
When the browser sees this header it will allow https://localhost:5001 to make HTTP requests to the server.
Building the Blazor WebAssembly client
Blazor provides two hosting models, Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server. In WebAssembly projects the app, dependencies, and the .NET runtime are downloaded to the client-side browser. In the Blazor Server model the app is executed on the server from within an ASP.NET Core app and the user interface in the browser is updated using SignalR.
The client project for this application will use Blazor WebAssembly so the client can function independently of the server and the Twilio and other JavaScript libraries can be executed on the client machine.
Create a Blazor WebAssembly project
Use the following commands to create the Blazor WebAssembly (WASM) project using the .NET blazorwasm project template:
Tip: If you’re building your solution with Visual Studio 2019, you can run this command in the Developer PowerShell window. Be sure you’re in the directory where the solution (.sln) file is located.
You can run your client project by running the following command:
If you’re using Visual Studio to run your projects, use the Kestrel target instead of IIS Express.
For your convenience, you can also use the dotnet watch run alternative. This will automatically reload the .NET application as you edit. You can use this command to watch your project:
You can access the Blazor WASM client at https://localhost:5001.
Add JavaScript and CSS
Create a new folder at TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\js and create an empty JavaScript file at TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\js\dialer.js.
Update TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\index.html to load the new JavaScript file by adding the following HTML to the bottom of the <head> element:
Append the following CSS to the existing CSS file at TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\css\app.css:
This is all the CSS necessary for the dialer component you are about to create.
Create a dummy Dialer component
Create a new folder in the Blazor WASM client named Components and create a component file named Dialer.razor.
Update TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\Components\Dialer.razor with the starter code below:
The HTML and CSS of the Dialer component are completed, the stub .NET methods are wired up to the buttons, and the private fields are bound to render the component. The only things left to do are implement the C#, implement the JavaScript, and integrate both — which is what you’ll do later in this tutorial.
Add the new component to the bottom of TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\App.razor:
When you run the client you will see the fully-styled dialer component.
Installing the Twilio Client JS SDK
The Twilio Client JS SDK contains functionality to connect to Twilio and make VoIP calls from JavaScript client applications.
To get started you can install the twilio-client npm package. Twilio strongly recommends including twilio.js in your applications via npm before going to production. Learn more in the Twilio Client JavaScript SDK Changelog.
To make this tutorial more convenient, you can use twilio.js directly from the Twilio CDN.
Add the following Twilio CDN script reference before the js/dialer.js reference in TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\index.html:
You can learn more about the Twilio Client JS SDK in Twilio’s documentation.
Managing Twilio calls with JavaScript
Now that the Twilio Client JS SDK has been installed in the Blazor Client you can start using the library to manage calls.
Inside TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\js\dialer.js, you’ll need to add JavaScript functions that are accessible from .NET.
Declare a global variable called dialer or explicitly declare the dialer variable as a property on the window object, which achieves the same result. Initialize the dialer variable with an object holding the following properties and functions.
Add the following JavaScript code to TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\js\dialer.js:
Here’s an overview of the properties and functions inside of the dialer object:
device: Twilio.Device is a virtual phone, if you will. This class holds the functions to connect to Twilio, accept calls, deny calls, etc. On page load, an instance of Twilio.Device will be created and stored in window.dialer.device.
setupTwilioDevice: This function accepts a jwtToken argument, a JSON Web Token that is the authentication token necessary to connect to Twilio. This token also includes the necessary information for Twilio to identify your TwiML application holding your voice webhook URL. The jwtToken will be passed in from Blazor .NET after having been generated by your server project.
This function will call the setup function on the Twilio.Device instance, which will perform the authentication against Twilio.
setupTwilioEvents: This function configures all relevant events for the dialer component:
- ready: triggers when the
Twilio.Deviceis ready to make and receive phone calls after successfully authenticating with Twilio - error: triggers when any error occurs
- connect: triggers when an incoming or outgoing connection is established
- disconnect: triggers when the connection is closed
- incoming: triggers when there’s an incoming connection
- cancel: triggers when a connection was closed before it was accepted
When these events occur, the relevant information should be passed to the Blazor Dialer component in .NET so it can update its state appropriately. You’ll replace the stubs with functional code in a forthcoming step.
startCall: use this function to initiate a phone call to the specified phonenumber. This function accepts a phonenumber which will be passed to the connect function on the Twilio.Device instance. The phonenumber is passed as metadata to the voice webhook configured in your TwiML application.
This function is step 1 of the Figure 1: Workflow diagram for outgoing phone calls and initiates the entire workflow.
endCall: When there’s an active phone call, you can use this function to end the call.
It retrieves the active connection using the activeConnection function on the Twilio.Device instance. If the activeConnection function returns a connection, the disconnect function will be called on the connection which will close the connection.
acceptCall: When there’s an incoming phone call, you can use this function to accept the call. It retrieves the active connection using the activeConnection function on the Twilio.Device instance. If the activeConnection function returns a connection, the accept function will be called on the connection which will start the phone call.
rejectCall: When there’s an incoming phone call, you can use this function to reject the call. It retrieves the active connection using the activeConnection function on the Twilio.Device instance. If the activeConnection function returns a connection, the reject function will be called on the connection which will reject the phone call.
destroy: This function calls the destroy function on the Twilio.Device instance. It cleans up all event listeners, connections, etc. You should call this function to clean up any resources when removing the Dialer component from the Blazor application.
Integrating JavaScript with the Blazor Dialer component
Blazor introduced a way to call JavaScript functions from .NET, and .NET methods from JavaScript, a process referred to as JavaScript Interop.
Call JavaScript functions from the Blazor Dialer component
To invoke JavaScript functions from Blazor you need an instance of the IJSRuntime interface.
You can obtain an instance using ASP.NET Core Blazor dependency injection. If you want to have the IJSRuntime injected into a .razor component, use the @inject directive at the top of your component, like this:
There are two instance methods used to call JavaScript functions from .NET using the IJSRuntime class:
InvokeAsync: This method will invoke the specified JavaScript function. It has one required parameter: a string to specify which JavaScript function to run. After the required parameter, you can pass as many extra parameters as you need to. Those subsequent parameters will be passed along to the JavaScript function.
You also must specify the return type you are expecting to receive from the JavaScript function using the generic type parameter. Blazor will try to convert the JavaScript return value to the requested .NET type.
InvokeVoidAsync: As the name gives away, this method functions like InvokeAsync, but it doesn't return the JavaScript return value.
Note: Even though the JavaScript return value isn't returned to you, it is still converted to a .NET type and then discarded. This behavior will change in future versions so that the JavaScript return value isn't unnecessarily converted.
For more details on JavaScript interop, read Communicating between .NET and JavaScript in Blazor with in-browser samples.
Update TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\Components\Dialer.razor so an instance of IJSRuntime is injected by adding the following line below @inject ILogger<Dialer> logger:
Wire up the .NET methods in Dialer.razor so they call the relevant JavaScript functions using InvokeVoidAsync by replacing the existing methods with // TO IMPLEMENT comments using the following C# code:
The new code does the following:
StartCall: Invoked when clicking the “Call” button. Invokes the dialer.startCall JavaScript function and passes dialNumber (bound to input) as a parameter.
EndCall: Invoked when clicking the “Hang up” button. Invokes the dialer.endCall JavaScript function.
AcceptCall: Invoked when clicking the “Accept” button. The “Accept” button is only visible when the boolean field hasIncomingConnection is set to true. Invokes the dialer.acceptCall JavaScript function.
RejectCall: Invoked when clicking the “Reject” button. The “Reject” button is only visible when the boolean field hasIncomingConnection is set to true. Invokes the dialer.rejectCall JavaScript function.
Dispose: Not all Blazor components need to implement the IDisposible interface, but if you have some resources to clean up you should implement it. In this case, the dialer.destroy JavaScript function is invoked inside the Dispose method. You can’t await the async InvokeVoidAsync, but you can still call it and it will “fire and forget”.
Note: In .NET 5.0, Blazor supports IAsyncDisposable, so you can await the async method. You can see the implementation here in the companion repository.
Fetch the Twilio authentication token
Instead of returning a dummy string as an authentication token, you need to fetch the authentication token from the TokenController from the server.
Add a static HttpClient at the top of the code section of Dialer.razor and update the GetTwilioAuthenticationTokenAsync method to send a GET request to https://localhost:5003/token by inserting the following statement after @code:
Replace the body of the method so it looks like the following:
If you’ve been coding this solution in Visual Studio 2019, all your errors and warnings should be resolved at this point.
Call .NET methods from JavaScript
In addition to calling JavaScript functions from .NET, you can also call .NET methods from JavaScript. You must decorate the .NET methods you want to expose to JavaScript using the JSInvokable attribute.
You can call .NET instance methods, but you need a reference to the object before you can invoke its methods. You can create a DotNetObjectReference instance by calling DotNetObjectReference.Create. You need to pass in the object you want a reference to as a parameter. When a DotNetObjectReference is returned to JavaScript from a .NET method or passed to a JavaScript function, it is converted to a JavaScript object which you can use to call the methods on the .NET object.
The JavaScript object converted from a DotNetObjectReference instance has two functions to invoke .NET methods:
invokeMethod: Invokes the specified .NET method and returns the .NET value converted as a JavaScript value. The first parameter is the identifier/method name of the .NET method. Any subsequent parameters will be converted to .NET values and passed to the .NET method.
invokeMethodAsync: Invokes the specified .NET method and returns a JavaScript Promise. When the Promise is fulfilled, the Promise result will be the return value from the .NET method. The first parameter is the identifier/method name of the .NET method. Any subsequent parameters will be converted to .NET values and passed to the .NET method.
For more details on JavaScript interop, read:
The Blazor Dialer component needs to create a DotNetObjectReference pointing to itself and then pass it to a JavaScript function to store it.
In the TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client/Components/Dialer.razor file, add the following field declaration to the existing private member variables:
Modify the OnInitalizedAsync method so it looks like the following:
The Dispose method should dispose of the object reference, so add a statement so the contents look like the following:
The Dialer component invokes the JavaScript function dialer.setDotNetObjectReference, which still needs to be created.
Update the TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\wwwroot\js\dialer.js file so the beginning of window.dialer object looks like the following:
Once the dotNetObjectReference property is set you can call .NET methods on the Blazor Dialer component. Update the dialer.setupTwilioEvents function so every event calls back into the Dialer component.
Replace the existing setupTwilioEvents function with the follow code:
These .NET methods do not yet exist. Create the following .NET methods in TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client\Components\Dialer.razor by inserting the following C# code in the @code section between the fields and the existing methods:
Each of these methods which respond to events in the Twilio.Device will modify the local state and call the StateHasChanged method to trigger a re-render of the component.
Test the code
At this point you have a partially functional Twilio Voice client. To test this, run the client:
Open a second shell and run the server:
Open your browser and navigate to https://localhost:5001/. You can find the Dialer component at the bottom right.
At this point the virtual Twilio device is configured and the authentication was successful, but when you try to initiate a call you hear the following voice message:
“We are sorry, an application error has occurred.”
This is because no voice webhook URL is configured to route the connection. Your next step is to implement the webhooks.
Implementing voice webhooks
The client is completed, but calls are not going out or coming in due to the lack of voice webhooks. In this section you will do the following:
- Add a controller to route phone calls
- Add a controller action to route outgoing phone calls
- Add a controller action to route incoming phone calls
- Use ngrok to make your local server publicly accessible
- Configure voice webhook URL on TwiML application for outgoing phone calls
- Configure voice webhook URL on Twilio phone number for incoming phone calls
Implement outgoing phone calls webhook
Add the Twilio.AspNet.Core NuGet package to the TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server server project:
This library adds some convenient classes which help with implementing Twilio webhooks. Learn more at the Twilio.AspNet.Core GitHub repository.
Create a new controller at TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server\Controllers\VoiceController.cs:
Note how VoiceController inherits from the TwilioController class provided by the Twilio.AspNet.Core library. The TwilioController class provides the TwiML method which you can use to return VoiceResponse and MessagingResponse instances.
When the Blazor client connects to Twilio, Twilio will send an HTTP POST request to your webhook with many <form> parameters including the metadata passed along to Twilio.Device.connect JavaScript function. Your webhook creates a TwiML response that instructs Twilio to Dial the phone number in the to parameter from the phone number specified in the CallerId which is your Twilio phone number.
To quickly verify if this works and what it looks like, run the server again:
While the server is running, open a separate shell and run this command, replacing the value for To with your Twilio phone number:
The response should have an HTTP status code 200, and the response content should look like this:
Make the local webhook server publicly accessible using ngrok
Twilio can’t access your controllers and actions because your server is running on your local network. You can use ngrok to make your server public for testing. Ngrok is a free service that allows you to setup a TCP tunnel from your local machine to their publicly available service.
You run the ngrok CLI tool on your machine and ngrok will tunnel it to a URL which looks similar to https://66a605a7ced5.ngrok.io — with a different subdomain. Every time you start the ngrok tool, the subdomain is different, providing security for your local machine through obfuscation. For a reserved domain and other features, you can upgrade to a paid plan.
Once ngrok has been setup, run this command to make your server accessible to the public:
The output will show the public ngrok URLs. Run your server using a separate shell:
To quickly verify the ngrok tunnel is working, you can run this PowerShell command again but with the public ngrok URL:
The result should be the same as before.
Configure the TwiML application voice webhook
Now that your server is publicly available using ngrok, you can configure the voice webhook URL on your TwiML application.
Run the following command to update the voice webhook for your TwiML application:
Replace [YOUR_TWIML_APPLICATION_SID] with the SID of your TwiML application and change the subdomain of the ngrok URL to your ngrok subdomain.
In addition to setting up a tunnel, the ngrok tool also hosts a local dashboard and API on your machine which have a lot of useful data. By default, this dashboard is hosted at http://127.0.0.1:4040/.
Instead of copying and pasting the webhook URL and updating the voice webhook URL whenever you restart ngrok, you can automate this connection using PowerShell and ngrok’s local API.
Create a PowerShell file UpdateTwilioWebhooks.ps1 and insert the code below:
Make sure to replace YOUR_TWIML_APPLICATION_SID with your TwiML application SID.
Whenever your ngrok URL changes, you can update the webhook URL by invoking the script like this:
Test outgoing phone calls
The entire workflow for outgoing phone calls is developed. Test your application by opening separate shells to run these commands:
- Run the client using
dotnet run -p TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client - Run the server using
dotnet run -p TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server - Run ngrok to tunnel the server
./ngrok http https://localhost:5003 - Update the TwiML application voice webhook URL by running UpdateTwilioWebhooks.ps1
Now that everything is running, open a browser and navigate to https://localhost:5001/.
Click the Show phone button on the bottom right, enter a phone number, and click the Call button. You should now be successfully calling the entered phone number.
Implement the incoming phone calls webhook
You are able to make outgoing phone calls, but still need to implement how to receive phone calls when your Twilio phone number is dialed.
Add an action for incoming voice calls to TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server\Controllers\VoiceController.cs:
When your Twilio phone number is called, Twilio will send an HTTP POST request to your webhook with form parameters including the phone number that is initiating the call in the from parameter.
Your webhook creates a TwiML response that instructs Twilio to Dial the blazor_client. This blazor_client string has to match the identity string specified on Token in the TokenController.
When Twilio receives this TwiML, Twilio will call all clients connected using blazor_client as the client name. The first client to pick up will establish a VoIP connection and the Dialer on the other clients will stop ringing.
To quickly verify if this works and see what it looks like, run the server again:
While the server is running, open a separate shell and run this command:
The response should have an HTTP status code 200, and the response content should look like this:
Configure the phone number voice webhook
To handle incoming phone calls you need to configure the voice webhook on your Twilio phone number. Just as before, make sure ngrok is running to tunnel your server:
Take note of the forwarding URL starting with https and use it to configure the webhook with the Twilio CLI:
Replace [YOUR_TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER] with your Twilio phone number and [YOUR_SUBDOMAIN] with your ngrok subdomain.
Alternatively, you can extend UpdateTwilioWebhooks.ps1 to also update the phone number voice webhook URL:
Test incoming phone calls
The entire workflow for incoming phone calls is developed. Test your application by opening separate shells to run these commands:
- Run the client using
dotnet run -p TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Client - Run the server using
dotnet run -p TwilioBlazorPhonecalls.Server - Run ngrok to tunnel the server
./ngrok http https://localhost:5003 - Update the webhooks by running UpdateTwilioWebhooks.ps1
Now that everything is running, open a browser and navigate to https://localhost:5001/.
With your real phone, call your Twilio phone number. The Dialer component should start ringing. Click the Show phone button and then click the Accept button. You should now be successfully calling your Blazor WASM application from your phone.
Take pride in your accomplishment and share it with your colleagues! 🙌
Enhancements and security warnings
This tutorial hardcoded some URLs and IDs. All these hardcoded values should be coming from external configuration. The source code in the GitHub repository for this tutorial uses ASP.NET Core’s configuration APIs to externalize configuration.
Currently, anyone who can access the server can request an authentication token to connect to Twilio. You can split the server into two servers, one for handling authentication tokens and one for handling webhooks. This way you can keep your token server on a private network while still serving your webhooks publicly.
Additionally, you should also add some authentication and authorization logic to the token controller so only authorized users can make and receive phone calls.
Since webhooks always need to be public, anyone could call them and potentially pretend to be Twilio making HTTP calls. To verify the HTTP calls are authentic and originate from Twilio, see Secure your C# / ASP.NET Core app by validating incoming Twilio requests in the Twilio docs.
If your Twilio phone number is called, but no clients are connected, the call will be cancelled abruptly which is confusing to the caller. The client could also be busy taking another call already, or the person could be too busy to pick up. You can specify a webhook URL on the Dial.Action attribute. Twilio sends a request to this webhook when the call has ended. You can use this webhook to send a proper response to the user using TwiML. Read Twilio’s best practices on how to gracefully handle no-answer situations. You can find code to do this in the project here.
You can implement this project using the new .NET 5.0 and C# 9 to take advantage of the latest improvements in the framework and language. There’s a complete version of the project with some of these features in the dotnet-5 branch of the companion repository.
Summary
In this tutorial you learned how to:
- Use the Twilio CLI to buy phone numbers, create TwiML applications, and update webhook URLs
- Create a ASP.NET Core controller to generate Twilio authentication tokens
- Call JavaScript functions from .NET in Blazor WASM
- Call .NET functions from JavaScript in Blazor WASM
- Use Twilio Client JS SDK to make and receive phone calls from the browser
- Route incoming and outgoing phone calls using TwiML and webhooks
- Make your local server publicly available using ngrok
You also got a few tips for turning this demo code into a secure production application.
Additional resources
Check out the following resources for more information on the topics and tools presented in this tutorial:
Communicating between .NET and JavaScript in Blazor with in-browser samples – This article walks you through JavaScript interop with live samples in the browser.
Call JavaScript functions from .NET methods in ASP.NET Core Blazor – This .NET documentation explains how to call JavaScript functions from .NET in Blazor.
Call .NET methods from JavaScript functions in ASP.NET Core Blazor – This .NET documentation explains how to call .NET methods from JavaScript in Blazor.
Twilio API: Access Tokens – This documentation guides you through generating access tokens granting access to voice, chat, and video functionality in Twilio.
Browser Calls with C# and ASP.NET MVC – This tutorial shows you how to make an ASP.NET MVC app to make voice calls from the browser
Niels Swimberghe is a Belgian Full Stack Developer and blogger working in the USA. Get in touch with Niels on Twitter @RealSwimburger and follow Niels’ blog on .NET, Azure, and web development at swimburger.net.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


