Build A Daily Sales Report Email Job Using Twilio SendGrid and .Net Azure Functions
Time to read:
Build A Daily Sales Report Email Job Using Twilio SendGrid, Azure SQL and .Net Azure Functions
Introduction
Reporting and notifications are crucial across industries for tracking progress, sales, and performance. One common example is a sales summary report, which consolidates the total amounts and number of items sold over a specific period. In this tutorial, you will learn how to build a daily sales report summary from an Azure SQL database table and send this summary via email.
Prerequisites
In order to be successful in this tutorial, you will need the following:
- A free Twilio SendGrid account
- Visual Studio free Community Edition
- Free Azure account
- Free Azure SQL database
- Microsoft SQL Management Studio
Building the app
You will start by creating the application in Visual Studio. Then you will include your database connection string in the application, so that the application can track the daily sales saved in the SQL database.
Visual Studio function app setup
Open Visual Studio. Click on Create a new project, then search for Azure Function. Click Azure Functions and click Next.
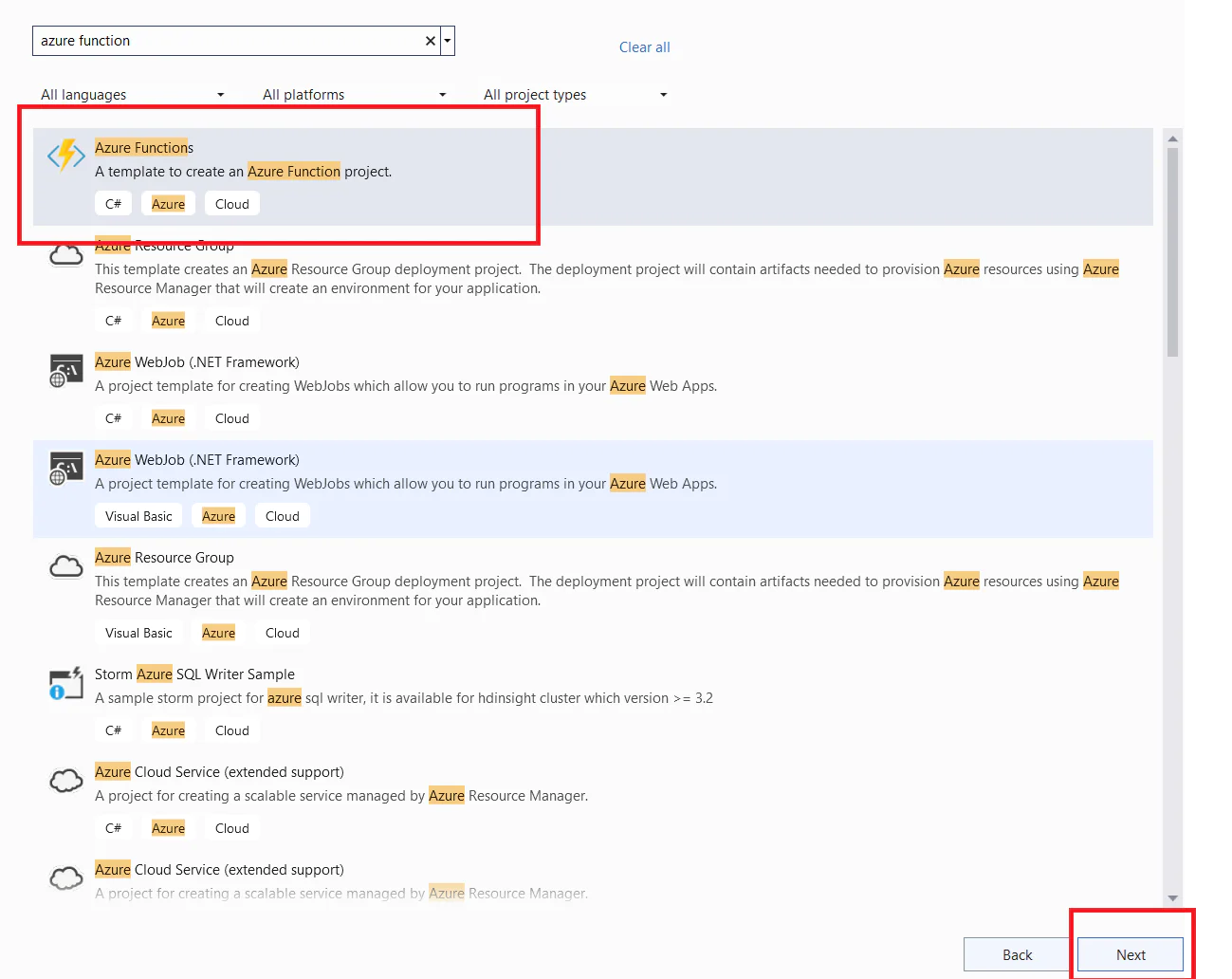

Name your project SalesReportJob and click Next. Then select the .Net runtime as .Net 8 and the function type as Timer trigger. You also need to set the schedule for when the job is going to run with the format of: {second} {minute} {hour} {day} {month} {day of week}. Set it as 0 0 * * * *, which corresponds to daily at 12 AM. Then click Create.
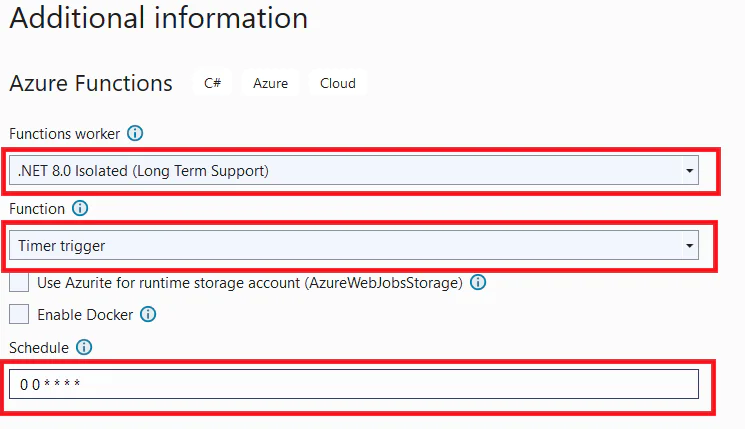

Retrieve your database’s connection string from the Azure portal by following the guidelines here . Then get back to Visual Studio, and add the connection string to local.settings.json file as shown below.
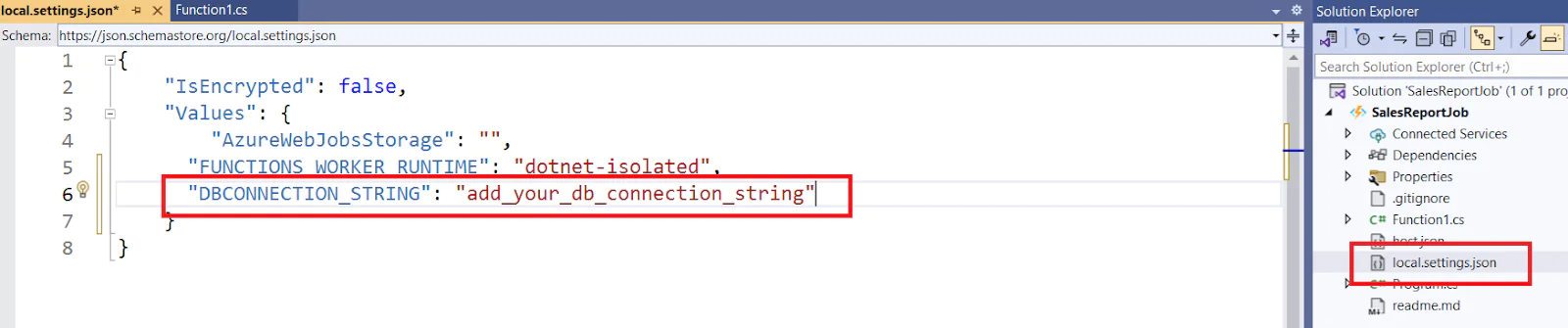

SendGrid API key
Before you can start sending emails, there are a few more mandatory steps you’ll need to complete.
- Verifying your Email
- Setting up 2-Factor Authentication
- Verifying your Domain
Once you’ve completed the above steps, you’ll need to create a new API Key . Keep this key somewhere safe as you will need it in the subsequent steps.
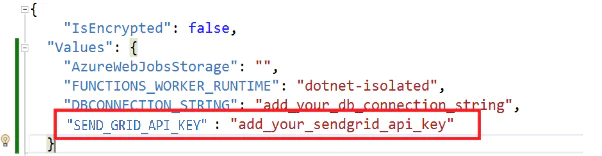
Go to the file local.settings.json and add the API key as shown below

Create SQL sales tables
Next, you need to open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to your Azure SQL database following the guidelines here. Make sure to allow public access in the SQL server on Azure portal by clicking on Security > Networking, then enable the option to allow public access. Then, right click the database and click on New Query. Add the following script to create two tables, one called Sales and the other called DailyReports, as shown below. Click Execute to run the queries.
Then, add some sample data to the sales table for the previous day to be able to test the job when the processing is done. Paste the following into a new query, and click Execute to run the queries.
Add necessary packages to Visual Studio
In order to be able to get and save data from/to your SQL server, you need to install a Nuget packet called “SQL Client." Click on Tools -> Nuget Package Manager -> Manage Nuget Packages For Solution.
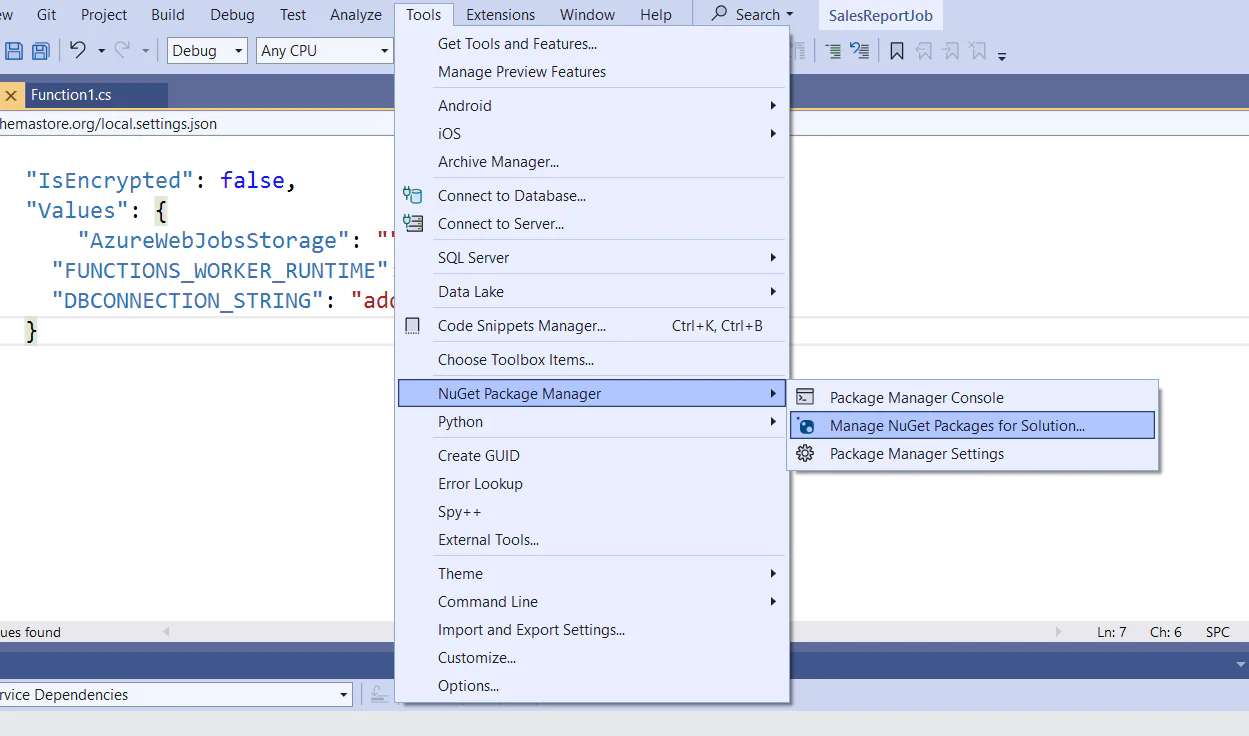

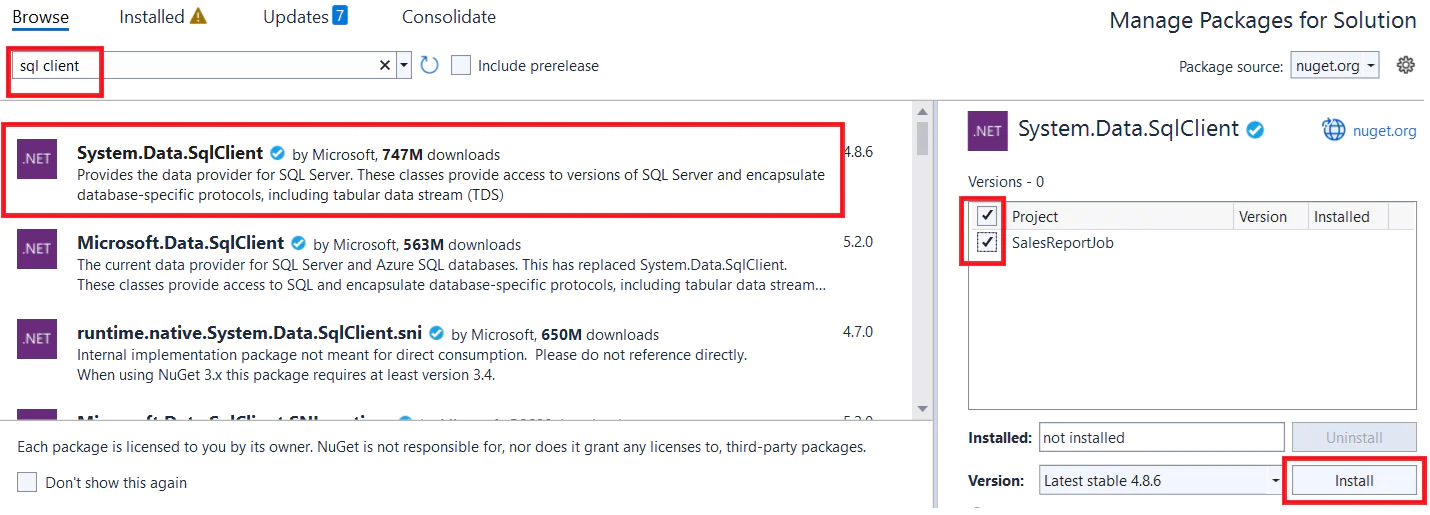
Then browse for the SQL Client package and install it to the project as shown below.

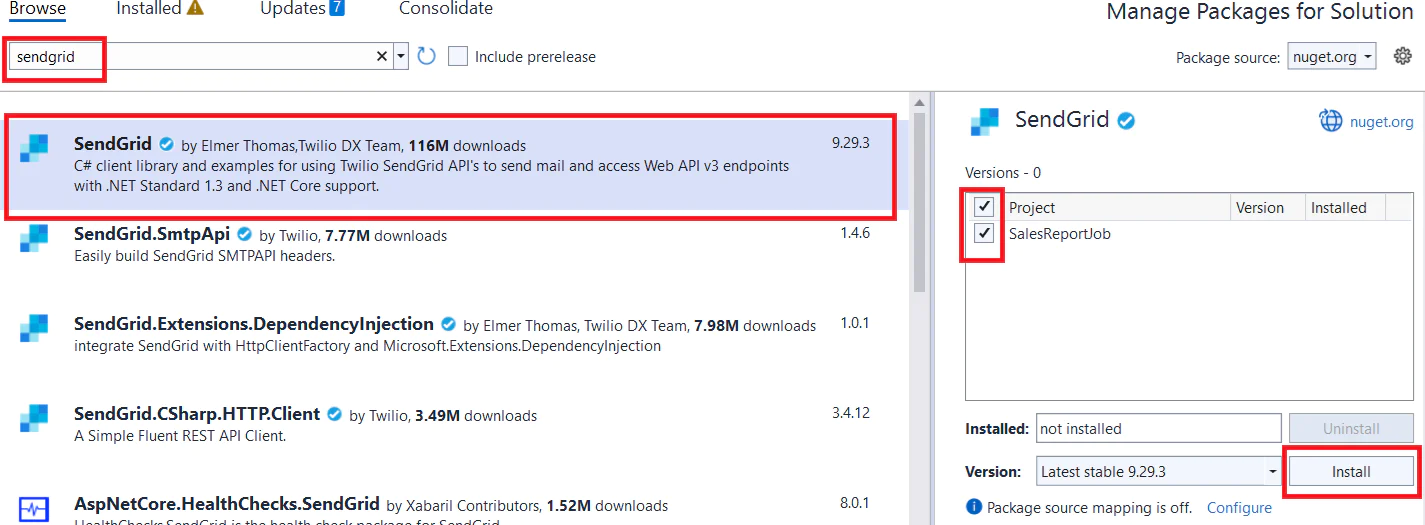
You need to also install SendGrid’s package as shown below.

Function Implementation
Rename the file Function1.cs to Total.cs. Replace the file’s content with the following code. This code adds the queries to select the total amount from the Sales table on yesterday’s date, then connects to the database and saves these amounts to the DailyReports table. It is configured for local testing, so if you are in DEBUG mode it will run the job immediately without having to wait until 12 am to run.
After the database query saves successfully an email needs to be configured to send that day’s total amount of sales. Replace the content of the sendEmail function with the following code:
You will need to add your to email to the variable toEmail by replacing add_your_email,and add the verified from email to the variable from by replacing add_verified_from_email
Testing the application
Before running the application locally, you need to go to local.settings.json and replace the value of AzureWebJobsStorage with : "UseDevelopmentStorage=true". Then add another item AzureWebJobsDashboard with the value: “UseDevelopmentStorage=true”


You can now run the job by clicking on the project’s name in the toolbar
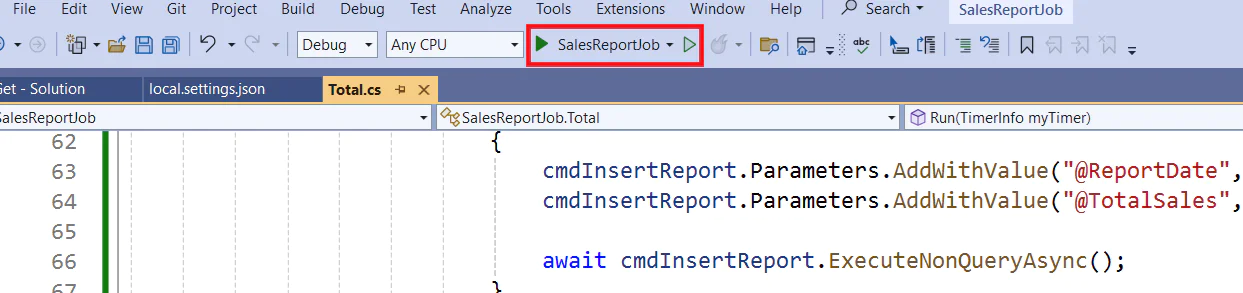

Then after running successfully it will show a log as shown below.
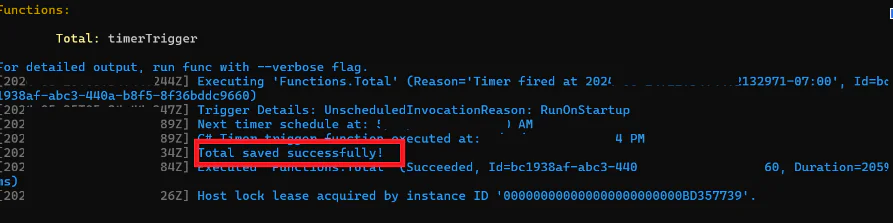

You can now validate that it ran successfully by checking your email and see the total: 200.5 from the records you added in the SQL database.
Publish the function to the Azure portal
In order to publish the function to start running daily on Azure, you need to login to the Azure portal . Search for “function app” then click on Function App.
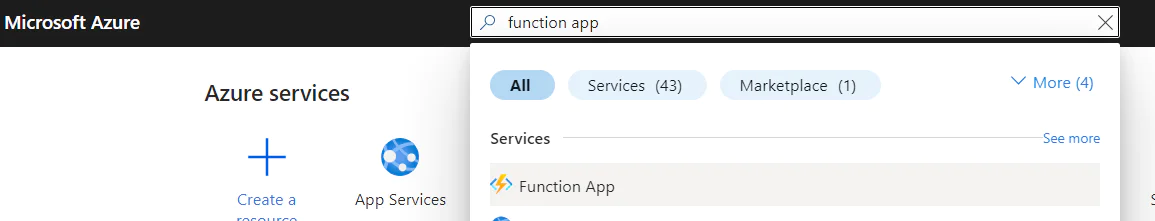

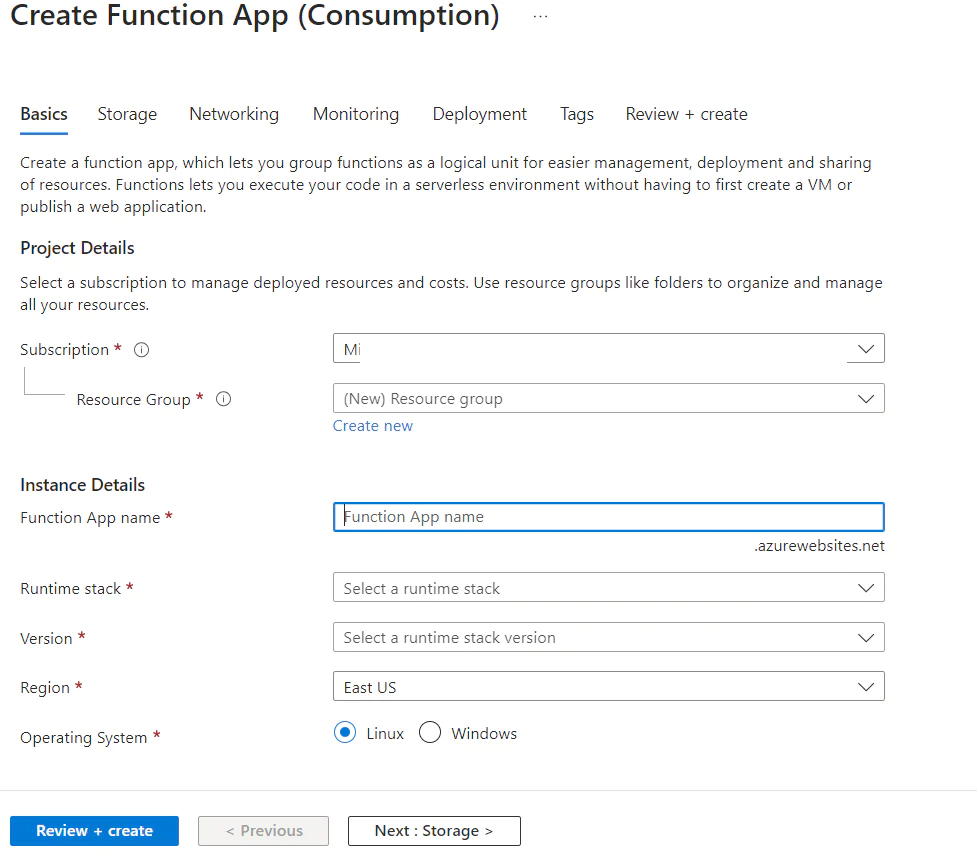
It will take you to the Azure functions window. Click Create to create a new function app.

You can then choose the hosting plan as a Consumption plan. This allows you to pay only when the function executes. Azure gives you the first 1 million executions for free according to the guidelines mentioned here .

Then add the basic settings as shown below:
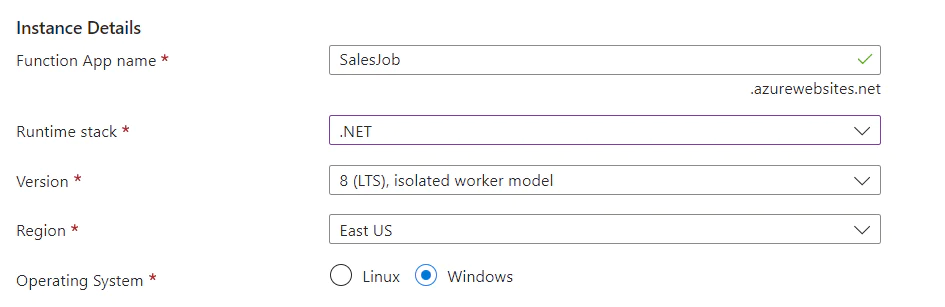

The tabs at the top show other aspects of your function app, but you don't need to change any of the default values. Keep clicking Next until you reach the tab: Review + Create. Click Create.

It will take a few moments to create the resources for you. When it is done, Azure will notify you that the resource has been created successfully. Click on Go to the resource on the notification popup.
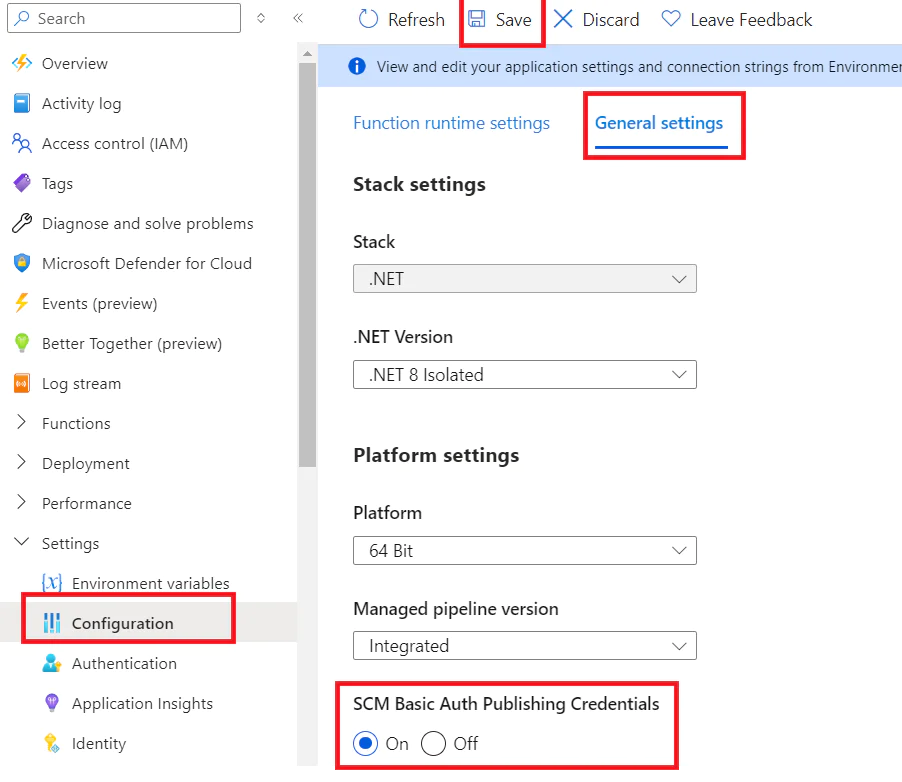
In order to be able to publish your code, you need to go to Settings -> Configuration -> General Settings and set SCM Auth Publishing Credential to ON. Click Save. Your app may need to restart to complete this process.

In the overview tap click on Get publish profile, and download the file. This is the file that you will attach to Visual Studio to be able to access the function app and publish your local job to Azure.


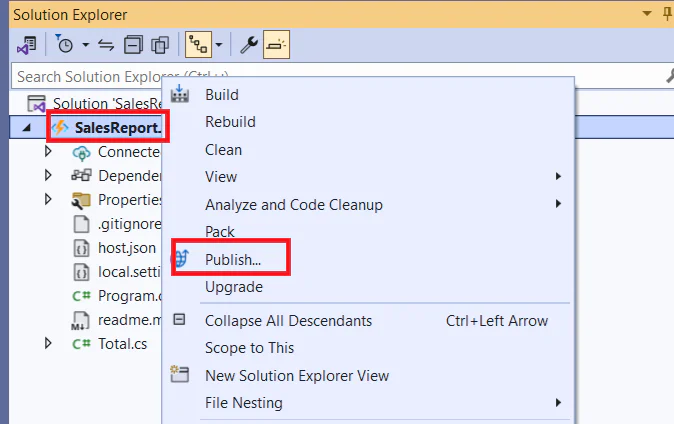
Go back to Visual Studio. Right click on the project name and click Publish.

Click on Import Profile and attach the publish profile that you downloaded from the Azure portal. Then click Finish.

You can now click on Publish on the main publish window. It will show the following output when the publish is complete.

Add connection strings and API Key to Azure
Since the file local.settings.json is only for local settings, you need to also add the SQL database’s connection string and SendGrid’s API key to Azure.
You can do this by clicking on the function app. Then go to Settings -> Environment variables and add these keys: DBCONNECTION_STRING and SENDGRID_API_KEY with the same name and value as you configured in your local file.
Security and maintainability considerations
A better way to secure your API keys and database connection strings is through Azure key vault instead of using environment variables directly. This will make this sensitive data more secure.
Another thing to keep in mind is that it is recommended to separate the SQL queries in stored procedures or use Object Relational Mapper (ORM) like Entity framework to query from and to the database, this is necessary to avoid threats like SQL injection .
To make sure your Azure Function is running properly, make sure you configure unit and integration testing . This is necessary especially when you have multiple Azure Functions running for different use cases.
Wrapping Up
At the conclusion of this tutorial, you will have acquired the skill sets to: set up and utilize Twilio SendGrid APIs, and create, configure and run an Azure function using C#. You can find the code project on github here .
Eman Hassan, a dedicated software engineer, prioritizes innovation, cutting-edge technologies, leadership, and mentorship. She finds joy in both learning and sharing expertise with the community. Explore more on her Medium profile: https://emhassan.medium.com.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


