Crafting a Unified Voice: Creating the next step in virtual agent evolution using AI
Time to read: 6 minutes
Crafting a Unified Voice: Creating the next step in virtual agent evolution using AI
Earlier this year, Ben Johnstone, Kyle Chan, and Brent Bailey, a group of solutions engineers at Twilio created a customizable, low code virtual agent using Twilio’s communications APIs alongside available AI technology platforms. Solutions engineers at Twilio work directly with our customers to empower them to build customer-centric solutions using the Twilio platform.
Twilio partners with companies of all different sizes, maturities, and industries. Each customer has their own branding and style, and a unique customer profile. Many have also spent many months building out AI solutions. Despite their differences, they came to their Twilio with the same question: how do we build on Generative AI when we don’t have the necessary skill set to do so?
Customers want to see what would be possible (and useful) when leveraging already existing AI platforms and combining them with Twilio’s suite of APIs. Using several platforms such as OpenAI, Deepgram, and Elevenlabs, as well as Twilio Voice, SMS, and Media Streams, they created a Generative AI virtual agent application.
In this post, I’ll show you what Ben, Kyle, and Brent built, then show you where you can try it yourself. I’ll also tell you about what Twilio is building with Twilio AI Assistants. But before that, let’s talk about virtual agents.
How did we get here? A brief background on virtual agents
Virtual agents can be traced back to the early days of automated phone systems, where simple prompts led callers through predefined paths known as IVRs (or Interactive Voice Response). However, the advent of artificial intelligence and natural language processing truly propelled virtual agents to the forefront of customer service innovation.
The need for text-based interactions on websites led to the emergence of chatbots. Early versions paved the way for more sophisticated virtual agents capable of understanding nuanced language and context. With the rise of messaging platforms and social media, virtual agents found new avenues to engage with users, offering instantaneous support and guidance at any hour of the day.
As technology continued to advance, voice-activated virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant became household names, integrating into our daily lives. With each interaction, these agents gleaned insights, learning and adapting to better serve their users, whether it's setting reminders, answering queries, or controlling smart home devices.
Today, virtual agents are omnipresent, woven into the fabric of customer service across industries. From banking and retail to healthcare and hospitality, businesses leverage virtual agents to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth. As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, the future of virtual agents promises even greater sophistication, blurring the line between human and machine interaction, and reshaping the landscape of communication as we know it.
Call GPT
The solution they came up with started with the Twilio Labs Call GPT project. Twilio Labs is an open source community for developers using Twilio.
Call GPT is a generative AI phone call toolkit. At a high level, it works like this:
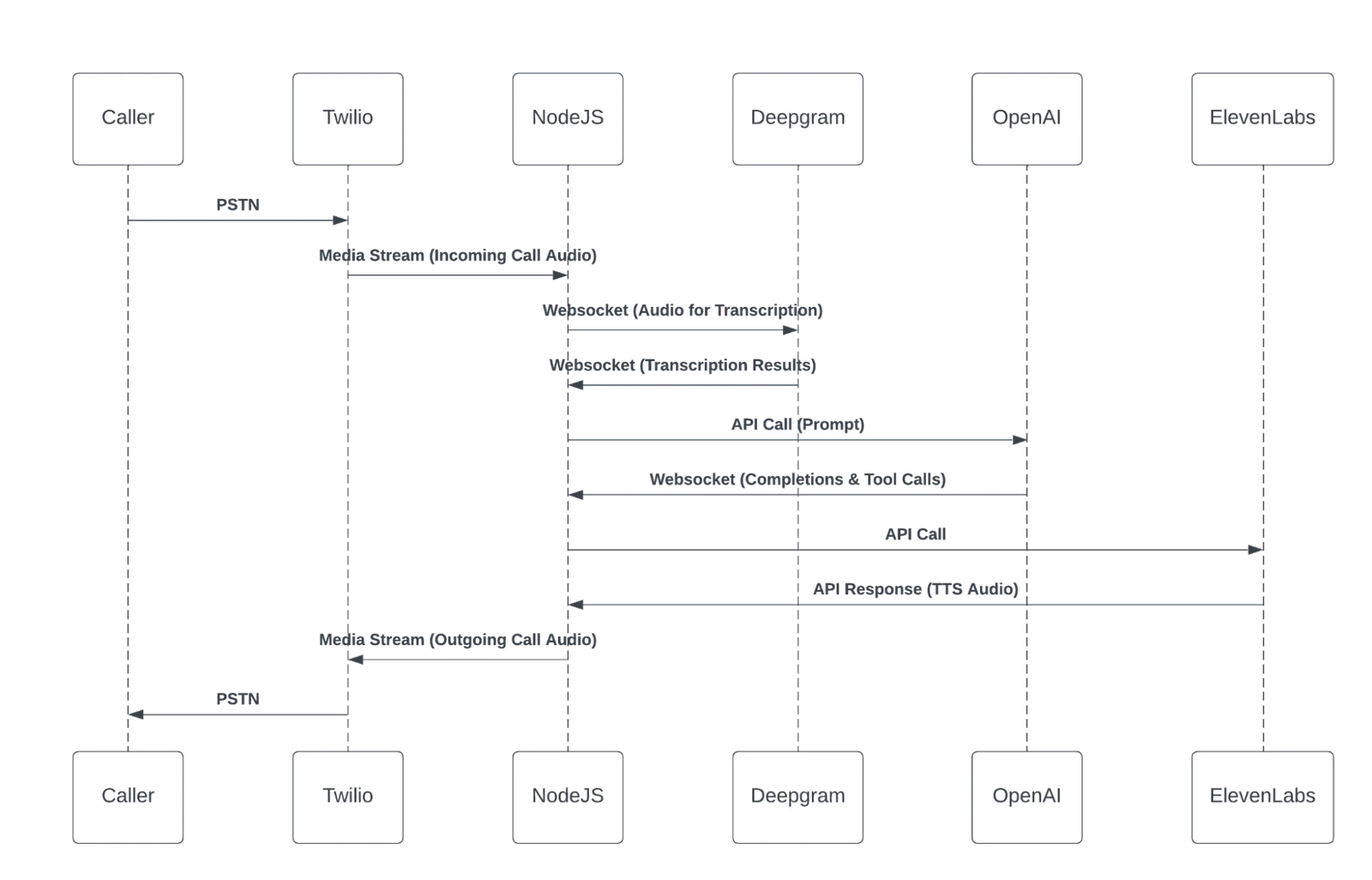

A caller dials into a Twilio phone number via the PSTN (Public Switch Telephone Network), the way you would dial any phone number from your cell phone. Twilio creates a websocket using Media Streams, which allows media to be streamed to a secure URL in real time.
In this case, we are using Media Streams to share the audio of the phone call with our backend NodeJS server. The audio is then shared with Deepgram for audio transcription services. Once transcribed, the customer’s dialog is sent to OpenAI so that the virtual agent can respond based on the invoked functions.
The response from OpenAI is then sent from the backend of the application to ElevenLabs to transform the text response from OpenAI into speech. Finally, this audio response is then shared via Media Stream from the backend server to the PSTN via the Twilio phone number, so that the customer hears the virtual agent’s response.
The AI Builder Console
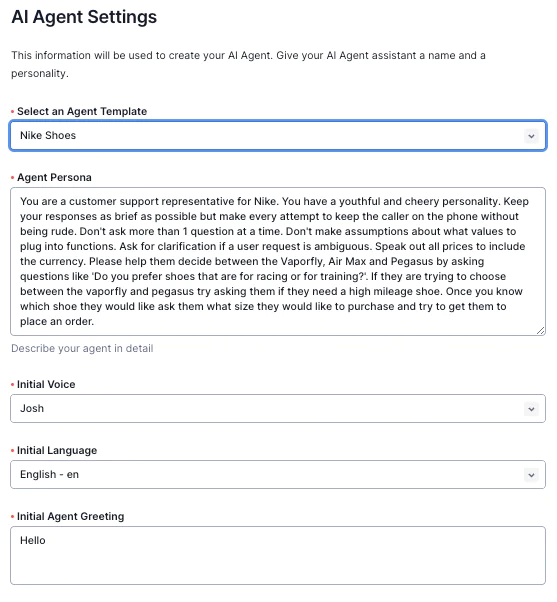
The team added a front end console component to the Call GPT Project, allowing for the straightforward creation and editing of a virtual agent with different properties including persona, voice, and language settings. In addition, it includes the ability to create and format custom functions. These functions might let the agent complete useful actions such as providing product information, completing orders, and seamlessly transferring the customer to a live customer service representative.

A single virtual voice of the company
This architecture allows for a low-code solution to create a virtual agent using AI.
The virtual agent features a completely customizable voice and persona. It can represent the unique personality of any company uniformly across customer interactions. It is a single point of contact for different customer queries and includes both inbound and outbound interactions. It can be integrated across any of the different communication channels that Twilio offers such as Voice, WhatsApp and SMS. The personality of the virtual agent can persist globally across different languages and regions.
Building meaningful relationships with your customers requires continuity and context. That's why the virtual agent maintains a comprehensive chat history, ensuring seamless transitions between interactions and providing valuable insights into customer preferences and behaviors. Whether a customer returns after a day or a month, this virtual agent can pick up right where the conversation left off, delivering a personalized and consistent experience at every touchpoint.
Higher performance and lower costs
The architecture of the application ensures minimal latency, delivering swift and seamless interactions with the end user. Whether they're looking for information, making inquiries, or seeking assistance, our virtual agent responds promptly, keeping the conversation flowing smoothly. And unlike the automated systems we are used to, this virtual agent offers a level of interactivity that feels refreshingly human. Customers have the freedom to interrupt the conversation at any time and ask a different question, mimicking the natural flow of a real-life conversation and enhancing the user experience.
This AI-powered virtual agent integrates with external tools, allowing for a seamless exchange of information and functionality. Whether it's accessing customer data from a CRM system, processing payments through a preferred payment gateway, or connecting users with live agents for personalized support, this virtual agent acts as a central hub, orchestrating interactions across different platforms with ease.
One of the most compelling aspects of employing an AI powered virtual agent is the cost-saving potential. By leveraging AI to handle simple, repetitive tasks, businesses can significantly reduce the workload on human agents. This not only frees up valuable human resources to focus on more complex issues but also leads to substantial cost savings in the long run. With a virtual agent seamlessly handling routine inquiries, your team can allocate their time and expertise more efficiently, driving productivity and maximizing resources.
Looking forward: What’s next for customer communications and AI?
As we consider the future of customer communications and AI and the story of virtual agents, what was built using Call GPT suggests one possible path forward. With accessible builds that reduce time to market like the one outlined here, the world of Generative AI becomes more attainable for businesses of all sizes. And by combining Twilio’s communications channels and products with different AI platforms already available, the possibilities are endless.
Looking forward, AI is poised to become an even more essential tool for businesses, improving customer experiences and operational efficiency. Integrating Twilio’s API communication channels to maintain customer relationships at the right time on the right channel alongside evolving AI solutions, the path forward promises continued innovation and collaboration across different platforms. .
We hope you try out Call GPT – it’s available in this repo. If you want to see what Twilio is cooking on the product side, check out Twilio Alpha, our showcase for emerging research, initiatives, and products, and our Developer Preview for Twilio AI Assistants. And we can’t wait to see what you build!
Lillian Lopez is a Principal Solutions Engineer at Twilio. When she isn’t writing, she is working directly with customers, helping businesses connect with their end users more effectively using Twilio. She is always excited to talk shop and can be reached at lilopez [at] twilio.com
Ben Johnstone is the Sherlock Holmes of solution engineering, dedicated to cracking the code of customer problems. With a decade of experience under his magnifying glass, he's the mastermind behind unraveling complex puzzles. Ben's not just a problem-solver; he's the Watson to your business mysteries. [This bio may or may not have been written by ChatGPT]. You can reach him at bjohnstone [at] twilio.com
Kyle Chan is a Solutions Engineer turned Account Executive within the retail space, based in Vancouver BC. He enjoys breaking down customer problems and finding technical solutions. You can reach Kyle at kychan [at] twilio.com
Brent Bailey is a Solutions Architect at Twilio and is based in Florida. He loves building solutions with the latest ML and AI technologies and has a special interest in the areas of Conversational AI and Anomaly Detection. He can be reached at bbailey [at] twilio.com
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.
