Send messages when you’re back online with Service Workers and Background Sync
Time to read: 7 minutes
When you send an SMS message but your phone doesn’t have great signal it will continue to try to send the message in the background, even if you close the app. Pretty useful right?
In this post we’re going to see how to replicate this behaviour in a web application using the Background Sync API from the Service Worker.
What we need
To demonstrate the Background Sync API let’s build a feature into an existing application, a web based SMS inbox for a Twilio number. You may have already seen this app when we implemented web push notifications for incoming text messages.
To run the application, you will need:
- A Twilio account (sign up for a free account here)
- A Twilio number that can send and receive SMS messages (buy your number in your account portal here)
- Node.js to run the application (check out our Node.js setup guide here)
- Chrome to test this in (support is coming in other browsers, but is only live in Chrome so far)
Once you have those bits sorted, you can either download the application from GitHub or clone it using git.
Change into the directory and install the dependencies:
Copy the .env.example file to a file called .env and fill it in with your Twilio Account SID, Auth Token and your Twilio phone number.
You should now be able to start the application and test it out. Start it with the following command:
Open the application in your browser at http://localhost:3000. You can send yourself an SMS message using the new message form.
If you were to try to send a message with this application without a network connection then you don’t get quite the same experience.
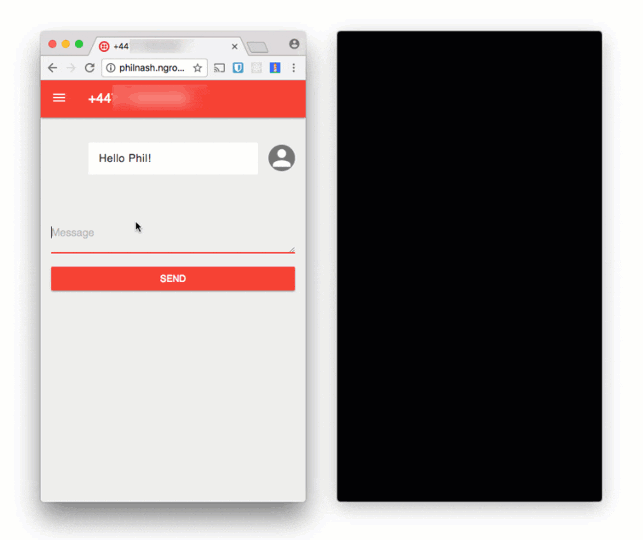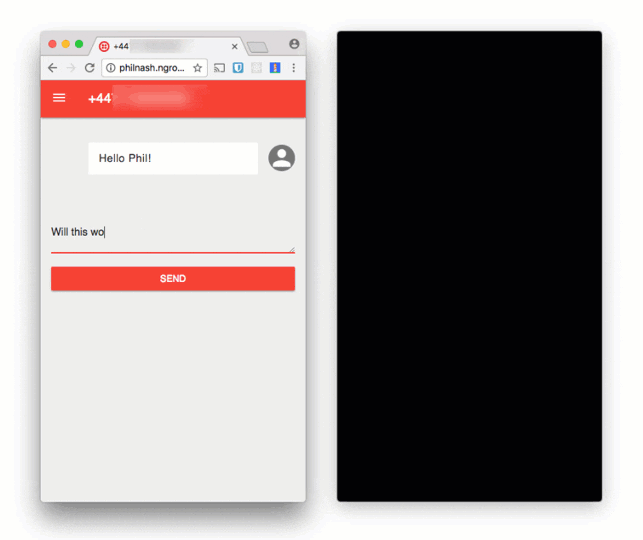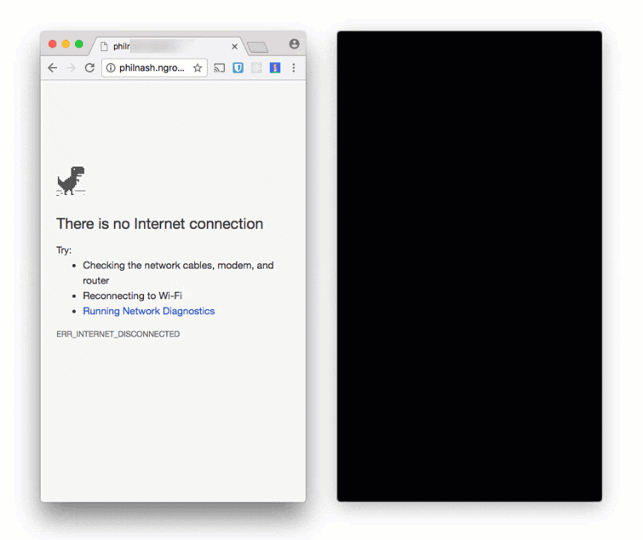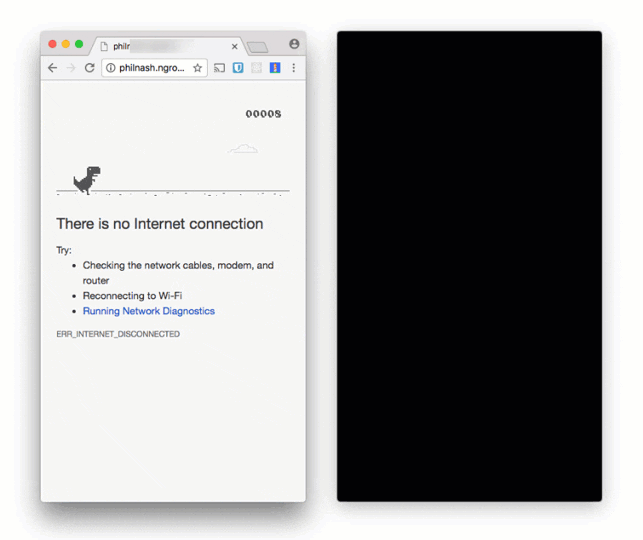
In fact, the experience is awful, but the Background Sync API can fix this. If we have a Service Worker and register for a sync event then the browser will only fire the event when it believes it has a good network connection. This allows us to store the messages we want to send while we are offline and only send them when the browser has a connection again.
What we are going to do
There are a few steps ahead of us to complete this task, so let’s break them down. On the page we need to:
- Register a Service Worker
- Intercept the “submit” event for our message form
- Place the message details into IndexedDB, an in browser database.
- Register the Service Worker to receive a “sync” event
Then, in the Service Worker we need to:
- Listen for sync events
- When a sync event is received, retrieve the messages from IndexedDB
- For each message, send a request to our server to send the message
- If the message is sent successfully, then remove the message from IndexedDB
And that’s it. We’ll get started with Service Worker registration.
Register a Service Worker
Create a new file called app.js in the public/js directory. Include it on the page by adding the following to the bottom of views/layout.hbs:
Open public/js/app.js and start with the following:
Once the content of the DOM has fully loaded this code will check whether the browser supports Service Workers as there’s no point carrying on if it doesn’t. Then it registers the Service Worker that will live in the file sw.js. When the Promise resolves and the Service Worker is successfully registered we then check to see if sync is supported too. Then we can really start to get to work.
Intercept form submit events
We need to get references to the form and the fields that we will read values from later. Then we listen for the submit event on the form so that when it triggers we can prevent it from actually submitting. Instead we’ll create a message object that contains the phone number and the body of the message that we can save to IndexedDB.
Saving the message to IndexedDB
Now that we have our message as an object we need to save it to IndexedDB so that the Service Worker can get it again later. We’re using IndexedDB to do this because the localStorage API, while simpler, doesn’t work in a Service Worker.
To make working with IndexedDB a little easier, I’m going to include Jake Archibald’s idb library which replaces the callback system with Promises. This has two benefits, the code to use the database is slightly less complicated and Service Workers expect to work with Promises so this prepares us for easier work later. If you aren’t familiar with Promises, check out Dominik’s guide to Promises.
I’ve already included the library in the project, so just add the following script tag to the layout before app.js.
Next we open up a database that we’ll call “messages”, in the callback we create an object store called “outbox” and tell it to use an auto-incrementing key which we’ll call id. When that Promise resolves we will have access to our database. We can then use it to start a transaction in our object store and put the message object into the store.
Once that database transaction completes successfully all we need to do is register for the sync event that we want the Service Worker to receive and tidy up our form.
Before we test this first part out we need to create a file for the Service Worker otherwise our initial install will fail and none of our code will run. Just create a blank file in the public directory called sw.js. Now, open up the message form, fill in a message and your phone number and click send. The form will clear but no message will get sent. If you open up dev tools and inspect IndexedDB from the Application tab you will find the message stored there safely.
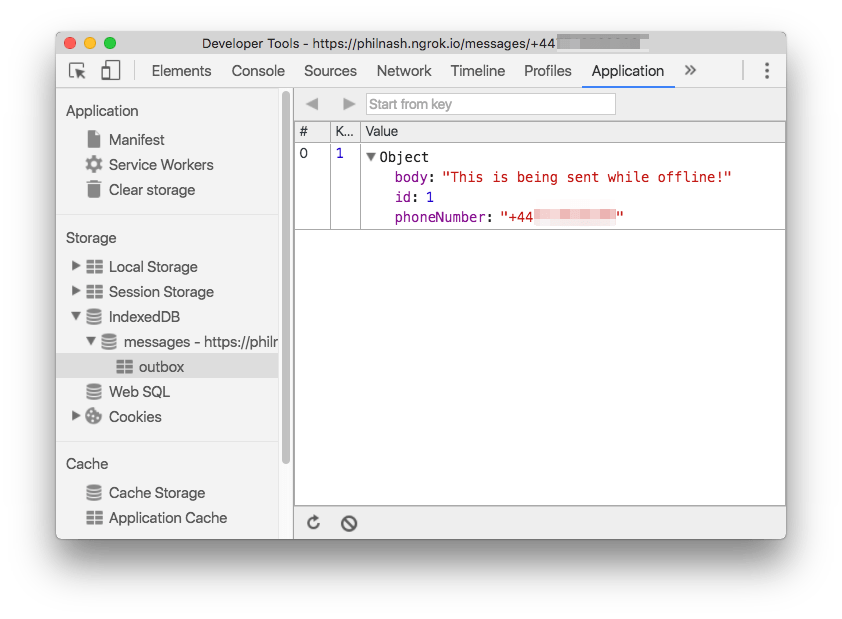
To make development with Service Workers easier for us, check the “Update on reload” checkbox under the Application tab of dev tools. This will save us having to deal with the Service Worker life cycle while in development.
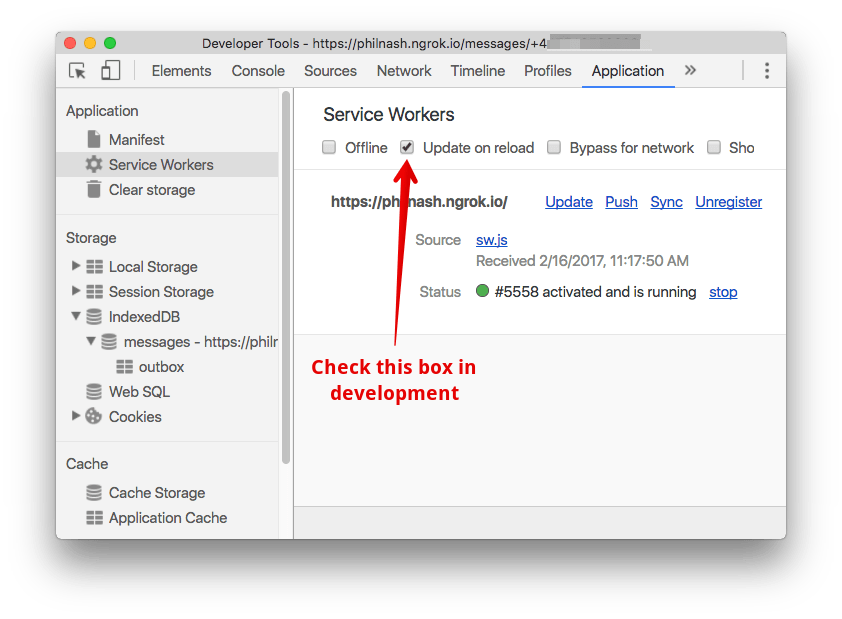
Now we need to implement the actual sync event in the Service Worker.
Implementing the sync event
Open up public/sw.js and start by importing the idb library and listening for the sync event.
Within the event listener we need to tell the browser to wait for the Service Worker to complete the asynchronous tasks of connecting to IndexedDB, retrieving any messages that need to be sent and sending them.
To do this we use the waitUntil method of the event, which takes a Promise as an argument and only completes when the Promise is resolved.
Time for a refactor
We need to connect to our IndexedDB database, but we already wrote the code to do that in our app.js file. This connection code can be refactored and shared between the Service Worker and the page.
Create a file called store.js in the public/js directory and enter the following:
The init function opens and upgrades the database if it needs it and returns a Promise that resolves with the database object itself. The outbox function returns a Promise that resolves with a reference to the object store for the outbox in the chosen mode (“readonly” or “readwrite”) within a transaction.
Add this script to the views/layouts.hbs.
Replace the use of idb in app.js with our new store.
Import our store to the Service Worker file.
Now we can use our store to get all the messages without repeating ourselves.
We have an array of messages to send. For each message we need to make a POST request to the original path, “/messages”, with the details of the message. Then we’ll read the response and if it is a success we’ll remove the message from the database.
As all those actions are asynchronous, we need to use Promise.all to wait for them all to successfully complete. That should look like this in sw.js:
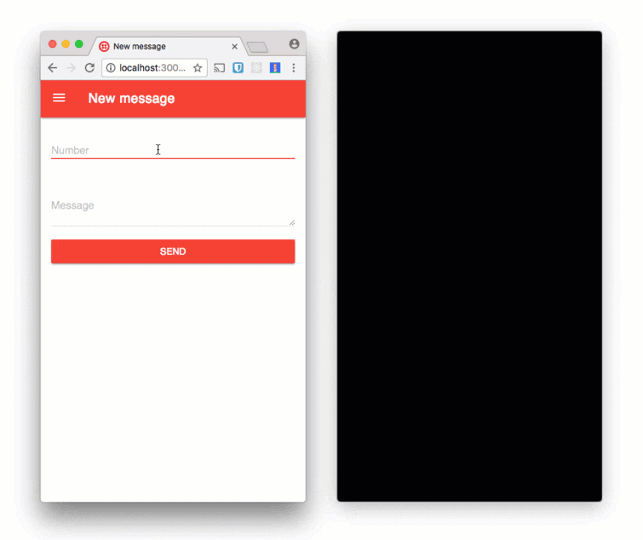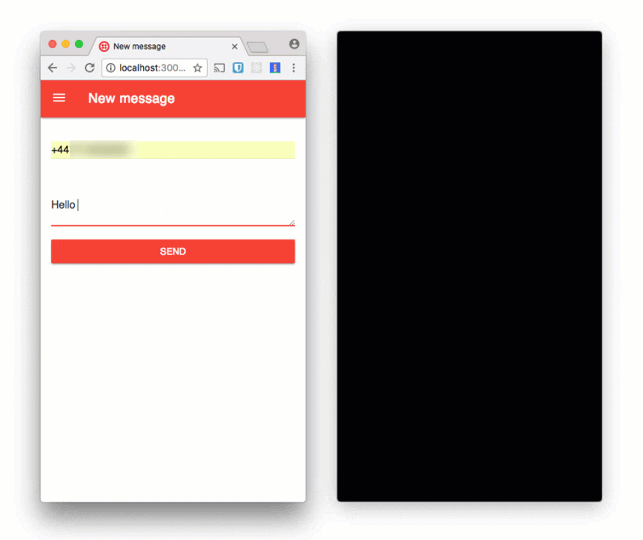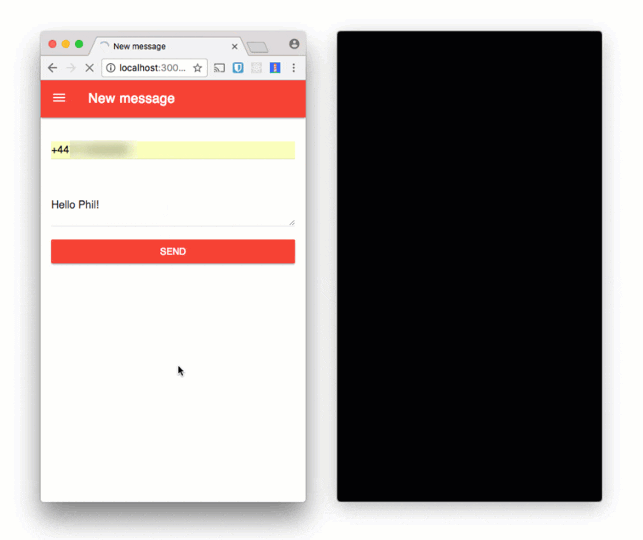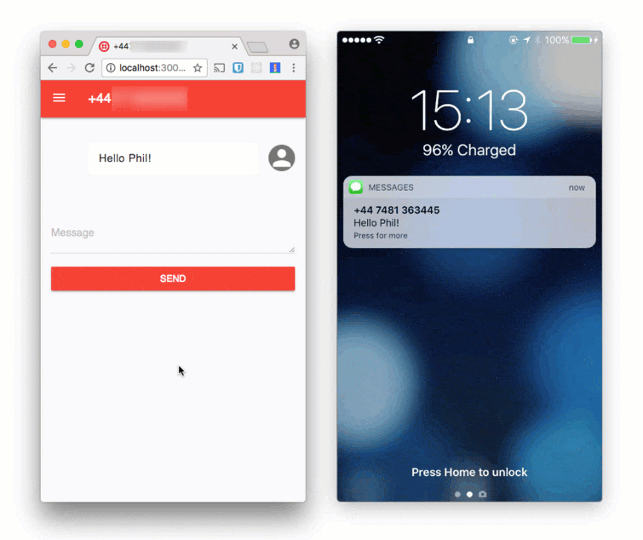
With all that in place we are ready to test. Reload the page and send a message. You should receive it straight away. You should also receive the first message you tried to send as that was waiting in IndexedDB too.
Now disconnect from the Internet and try to send a message. Wait a while, turn the network back on and whoosh, there go the messages!
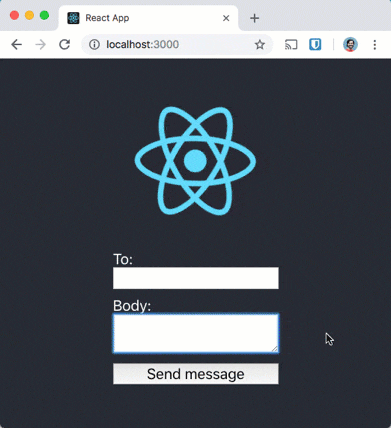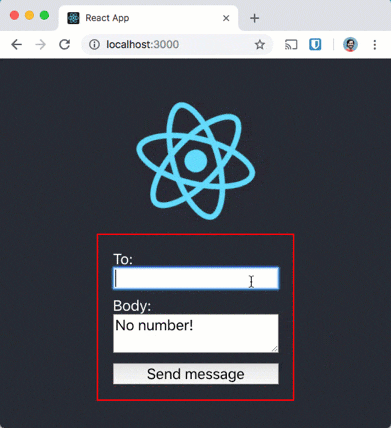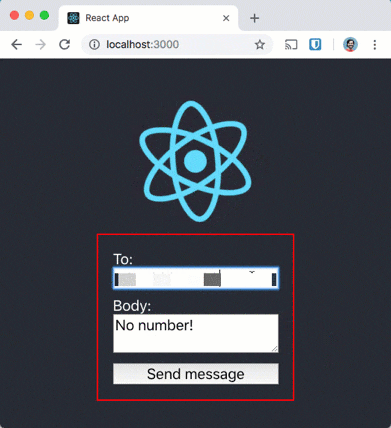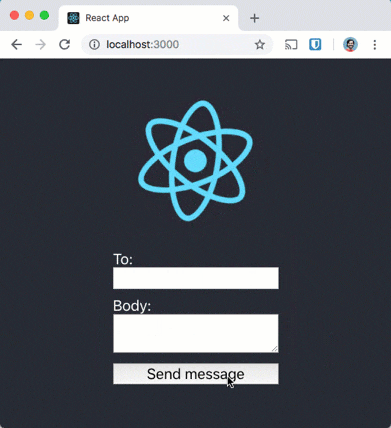
Network resilient messages
Using the Background Sync API for the Service Worker we now have network resilient message sending. No longer will users have to keep a web site open waiting to see if what they just did worked. We are getting closer to the experience that a native application can provide a user, like the built in SMS app I mentioned at the start.
This is just an initial implementation, the full code of which is on GitHub.
There are more places we can try to improve the user experience in this application too, like:
- Improving the UI to show messages that haven’t sent yet
- Including a timeout or method for cancelling sent messages
- Push notifications to notify about message failure
Sending messages is not the only use case for background sync either. I can see this being useful for things like:
- Adding items to a shopping cart
- Requesting a callback from a web form
- Downloading an article in the background (see Jake Archibald’s Offline Wikipedia project for an example)
- Creating channels, sending messages, inviting users or any other action within a Programmable Chat application
I hope you’re excited about the potential for the Background Sync API, let me know what you think or if you have any ideas for what you might use it for. I can be reached in the comments here, on Twitter at @philnash or by email at philnash@twilio.com.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.